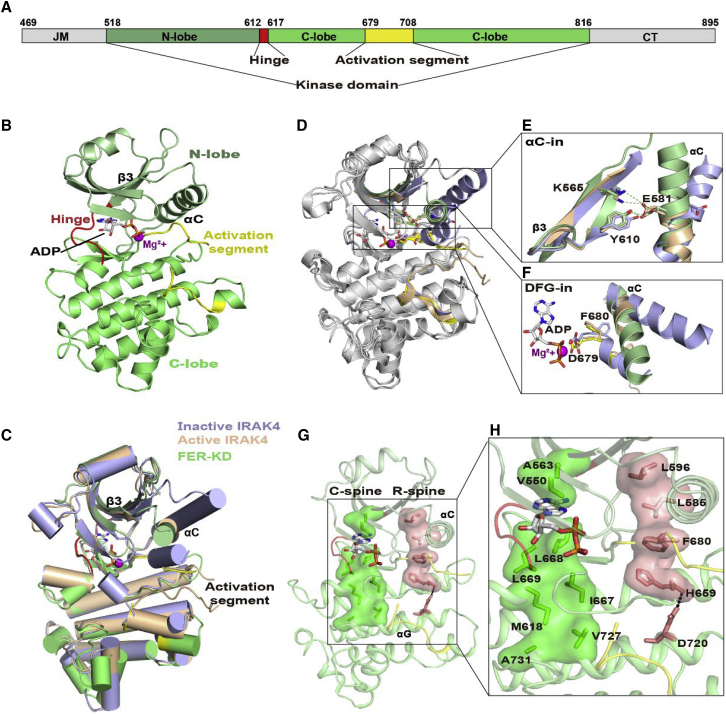
Figure 1.
Overall structure of FER-KD complexed with ADP.
(A) Schematic diagram of the FER fragments from the intracellular domain (FER-CD) in our study. JM, juxta-membrane domain (shown in gray); KD, kinase domain N-lobe is shown in pale green; C-lobe is shown in light green; the overall color is green); AS, activation segment (shown in yellow); CT, C-terminal tail (shown in gray). The hinge is presented in red. Residues located at the domain boundaries are numbered on top of the panel.
(B) The structure of FER-KD, as shown in a cartoon representation. The FER-KD color scheme is the same as that in the schematic diagram in (A). ADP is shown as colored sticks, and Mg2+ ions are indicated by purple spheres.
(C and D) Ribbon structural comparison of FER-KD (green) with active IRAK4 (wheat, PDB: 2OID) and inactive IRAK4 (light blue, PDB: 6EGF) in two views. The ADP and Mg2+ in FER-KD are presented as in (B). The AMP-PNP and ions in IRAK4 are not shown.
(E and F) Detailed comparison of the active sites with αC-in (E) and DFG-in (F). The essential residues are presented as sticks. The hydrogen bonds (between E581 and Y610) and salt bridges (between E581 and K565) in FER-KD and active IRAK4 are presented as green and wheat dashed lines, respectively.
(G and H) C-spine and R-spine in the FER-KD–ADP complex. The C-spine and R-spine are presented in green and salmon surface representations, respectively (G). The C-spine, comprising V550, A563, M618, I667, L668, L669, V727, and A731, is indicated by green sticks. The R-spine, consisting of L585, L596, F680, H659, and D720, is indicated by salmon sticks (H).