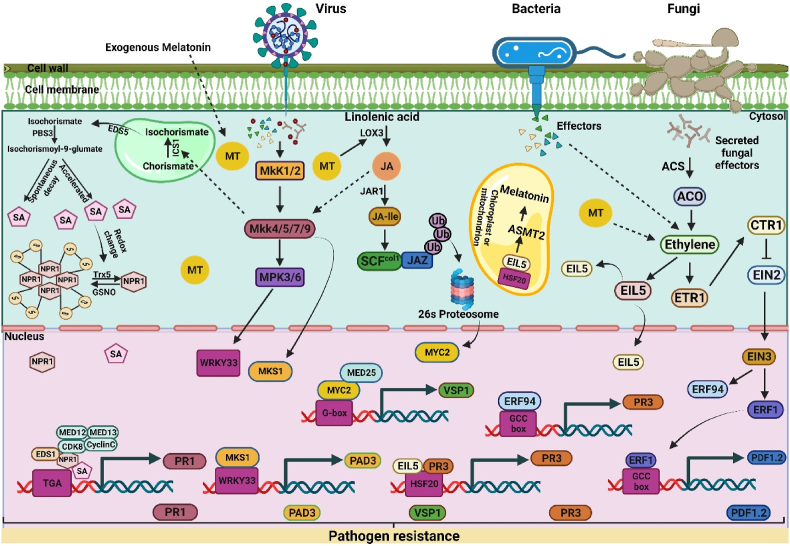
Fig. 6.
Schematic representation of melatonin (MT) interplay with salicylic acid (SA), jasmonic acid (JA), and ethylene (ETH) under phyto-pathogen invasion. (1) MT-SA interaction: A biotrophic pathogen invade plants by releasing effectors into the host cells. The exogenous application of MT up-regulates the ICS gene through mitogen-activated protein kinase (Mkk4/5/7/9). ICS is involved in the catalyzation and conversion of chorismite into isochorismate, and Enhanced Disease Susceptibility 5 (EDS5) exports this protein to the cytoplasm. As a result of PBS3's cytosolic activity, l-glutamate, and isochorismate are conjugated to synthesis isochorismate-9-glutamate. As a result of spontaneous decay, SA is produced from isochorismate-9-glutamate. In addition to acting as a Pyruvoyl glutamine lyase, the EPS1 may also be capable of breaking down N-pyruvoyl-l-glutamate into SA. As a result of the interaction between WRKY transcription factors and NPR1, CDK8 is recruited to the W-box sequence in the promoter of NPR1 gene. The MT-mediated over-expression of ICS and pathogen-induced defense signaling promote SA accumulation. Moreover, SA stimulates redox reactions through which NPR1 oligomers are reduced to monomers. NPR1 monomers migrate from the cytosol to the nucleus, forming an association with transcription factors (TGA), CDK8, EDS1, and SA, which results in the transcription of PR genes. (2) MT-JA interaction: Exo-/endogenous MT increases the endogenous level of JA via up-regulating the LOX genes. Pathogen-secreted effectors are recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRR), which stimulate the MEK1/2 cascades. MT triggers the activation of MKK4/5/7/9, and MKK4 induces the activation of MPK3/MPK6 and MKS1 (MPK4's substrate). Camalexin (a phytoalexin) is biosynthesized by the WRKY33 transcription factor. WRKY33 is phosphorylated by MPK3/MPK6, which enhances its transactivation activity. As a result of the complex formed between WRKY33 and MKS1, Phytoalexin Deficient 3 (PAD3) is transcribed, activating the camalexin synthesis. In elicited cells, SCFcol1 is formed by associating Col1 with SKP1, Cullin, and JA-Ile protein. The SCFcol1 ubiquitinates the JAZ family of repressor proteins and degrades these by the 26S proteasome. Degradation of JAZ stimulates downstream JA responses due to the release of MYC2 from inhibition. MEDIATOR25 (MED25) stimulates wound-responsive gene VSP1 transcription by bonding with MYC2. (3) Ethylene stimulates MT production: During invasion on plants, the necrotrophic pathogen releases its effectors into the plant's cell, resulting in the activation of genes encoding ethylene production, such as 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase (ACS) and 1-aminocyclopropane-l-carboxylic acid oxidase (ACO) that can produce ethylene. The addition of MT also stimulates the production of ethylene and up-regulation of ETHYLENE INSENSITIVE LIKE 5 (EIL5). The EIL5 directly binds with HEAT STRESS TRANSCRIPTION FACTOR 20 (HSF20) and leads to the activation of N-acetylserotonin O-methyltransferase 2 (ASMT2) gene, which produces the MT. The ethylene levels are low under control/normal conditions, leading to the activation of Ethylene receptor 1 (ERT1), which binds with CTR1 and suppresses the downstream signaling pathways. However, a higher level of ethylene inactivates Raf-like protein CTR1 by binding to its receptors and activating ethylene insensitive 2 (EIN2) and ethylene insensitive 3 (EIN3) transcription factors. EIN3 is responsible for regulating ERF1 and ERF94 expression. The ERF1 and ERF94 interact with the GCC box and activate PDF1.2 and PR3 genes, respectively. The higher protein concentration of EIL5 facilities the binding of the Hsf20 and PR3 and further promotes the synthesis of PR3, which triggers the pathogen resistance genes in the plant.