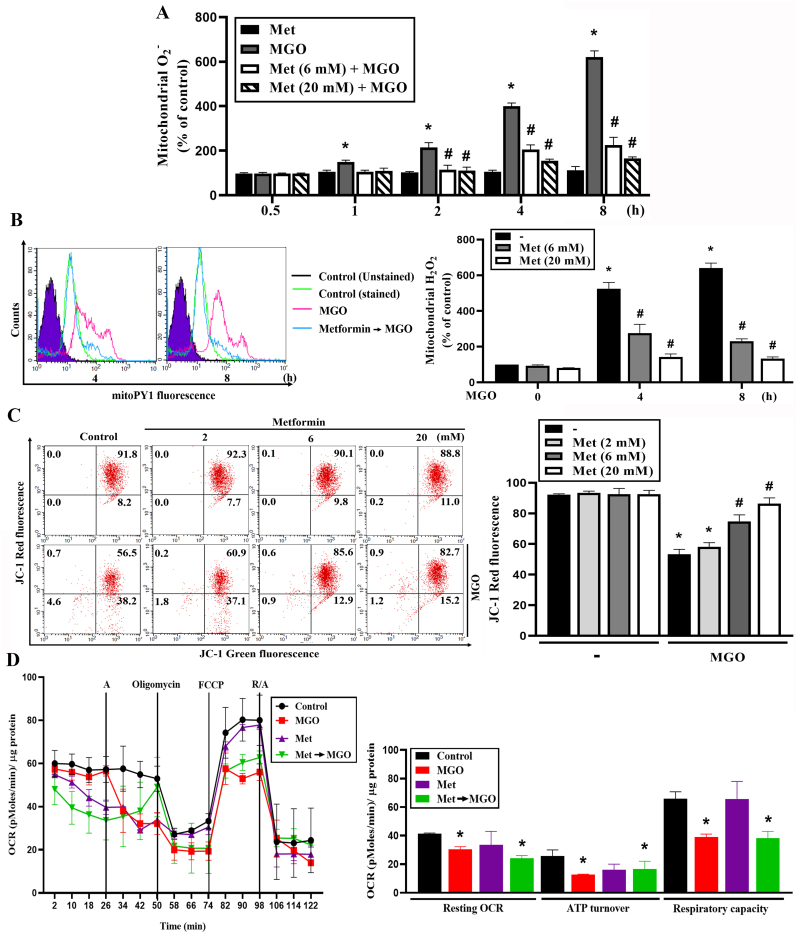
Fig. 3.
Metformin attenuates MGO-induced mitochondrial ROS production and mitochondrial membrane potential loss.
(A, B) Cells were 30 min pretreated with metformin (6 mM or 20 mM) followed by MGO (300 μg/ml) stimulation for indicated time points. Mitochondrial superoxide anion and mitochondrial H2O2 were measured using mitoSOX (A) and mitoPY1 (B) respectively. (C) Cells were pretreated with metformin (2, 6 or 20 mM) 30 min prior to MGO (300 μg/ml) treatment. Four hours later JC-1 was used to measure the mitochondrial membrane potential by FACScalibur. (D) Cells were treated with metformin (6 mM) and immediately subjected into Seahorse XFe24 analyzer. After 26 min MGO was injected through port A. Cells were subsequently treated with oligomycin (2.5 μM), FCCP (1 μM) and antimycin A (2.5 μM)/rotenone (2.5 μM) through parts B, C and D at 50 min, 74 min and 98 min, respectively. Intracellular OCR was measured by seahorse XF24 analyzer. Data were the mean ± S.E.M. from at least 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.05, indicating the significant effect of MGO. #p < 0.05, indicating the reversal effects of metformin.