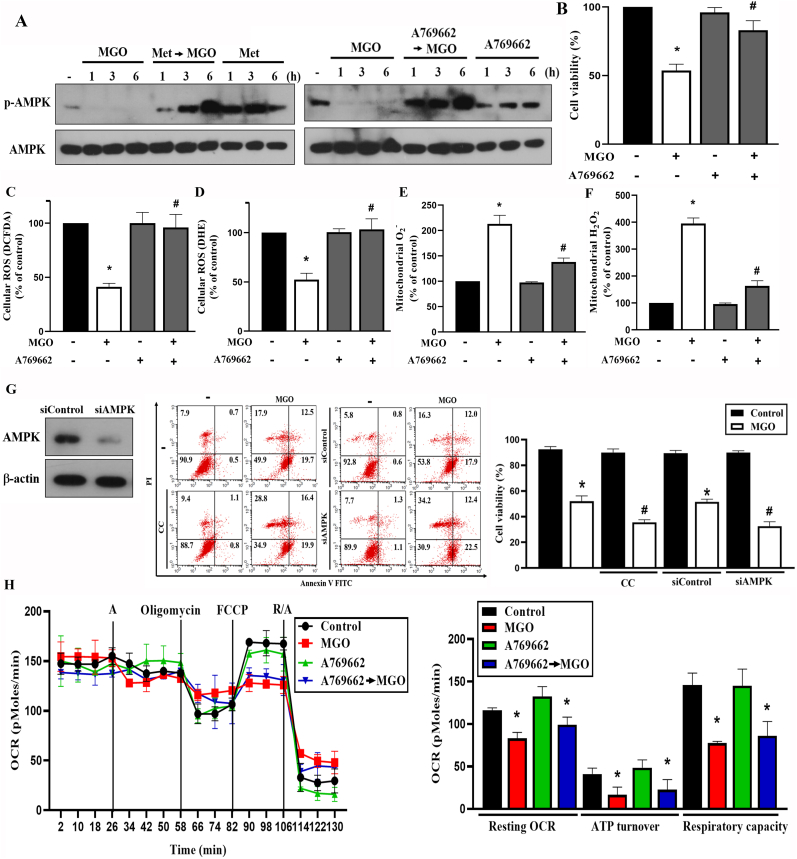
Fig. 5.
AMPK activator A769662 mimics the effect of metformin in MGO-stimulated cells
(A) Cells were pretreated with metformin (6 mM) or A769662 (25 μM) 30 min prior to MGO (300 μg/ml) treatment for indicated time points. AMPK phosphorylation was measured by immunoblotting. (B) Cells were 30 min pretreated with A769662 (25 μM) prior to MGO (300 μg/ml) for 6 h. Cell viability was measured by Annexin V-FITC/PI using FACS. (C, D, E, F) Cells were pretreated with A769662 (25 μM) for 30 min followed by MGO (300 μg/ml) treatment for 4 h. DCFDA (C), DHE (D), mitoSOX (E), and mitoPY1 (F) were used to measure cellular ROS. (G) Cells were 30 min pretreated with compound C (10 μM) followed by MGO (300 μg/ml) stimulation for 6 h. In some experiments, ARPE-19 cells were treated with siRNA followed by stimulation with MGO (300 μg/ml) for 6 h. Cell viability was measured by Annexin V-FITC/PI using FACS. AMPK expression after siRNA treatment was determined by immunoblotting. (H) Immediately after treatment with A769662 (25 μM), cells were subjected into SFe24 analyzer for OCR measurement, as described in Fig. 3D. Data were the mean ± S.E.M. from at least 3 independent experiments. *p < 0.05, indicating the significant effect of MGO; #p < 0.05, indicating the significant effects of A769662, compound C and AMPK silencing on MGO-induced responses.