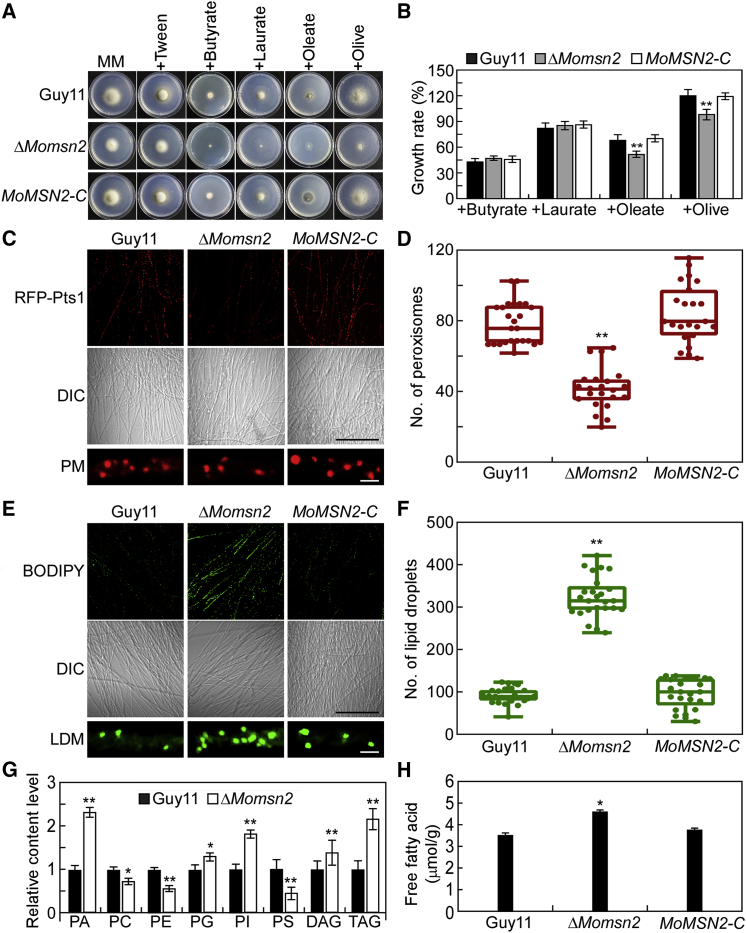
Figure 2.
MoMsn2 is involved in fatty acid oxidation.
(A) The wild type Guy11, ΔMomsn2 mutant, and complemented transformant MoMSN2-C were inoculated onto MM plates or MM with different fatty acids as carbon sources, cultured at 28°C for 7 days, and photographed.
(B) Statistical analysis of the growth rate of the indicated strains on different media. Error bars are SDs of three biological replicates, and asterisks represent significant differences by two-tailed Student’s t-test at ∗∗p < 0.01.
(C and D) The morphology and number of peroxisomes were examined and statistically analyzed in Guy11, ΔMomsn2, and MoMSN2-C strains expressing the RFP-Pts1 protein. Fluorescence images were taken using the 3D reconstructed confocal z stack method with 20 photos. Differential interference contrast images were taken under a confocal microscope. Quantitative analysis of peroxisomes was performed in 1 × 104 μm2 from 25 fields of view in each strain using ImageJ (Media Cybernetics, Shanghai, China), and the number of peroxisomes is represented by a box-dot plot. Statistical analysis was performed by two-tailed Student’s t-test using GraphPad Prism 8.0.1, and asterisks represents significant differences at ∗∗p < 0.01. PM, peroxisome morphology. Black scale bar, 100 μm; white scale bar, 1 μm.
(E and F) The morphology and number of LDs were examined and statistically analyzed in Guy11, ΔMomsn2, and MoMSN2-C strains stained with BODIPY 493/503. Fluorescence images were taken using the 3D reconstructed confocal z stack method with 20 photos. Quantitative analysis of peroxisomes was performed in 1 × 104 μm2 from 25 fields of view in each strain using ImageJ, and the number of peroxisomes is represented by a box-dot plot. Statistical analysis was performed by two-tailed Student’s t-test using GraphPad Prism 8.0.1, and asterisks represent significant differences at ∗∗p < 0.01. LDM, lipid droplet morphology. Black scale bar, 100 μm; white scale bar, 1 μm.
(G) High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)–mass spectrometry analysis of the lipid profiles of Guy11 and ΔMomsn2. DAG, diacylglycerol; PA, phosphatidic acid; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE, phosphatidylethanolamine; PG, phosphatidylglycerol; PI, phosphatidylinositol; PS, phosphatidylserine; TAG, triacylglycerol. Means and SDs were calculated from four independent replicates. Asterisks indicate significant differences by two-tailed Student’s t-test at ∗p < 0.05 and ∗∗p < 0.01.
(H) Quantification of free fatty acids in Guy11, ΔMomsn2, and MoMSN2-C. Error bars are SDs of three biological replicates, and asterisks represent significant differences by two-tailed Student’s t-test at ∗p < 0.05.