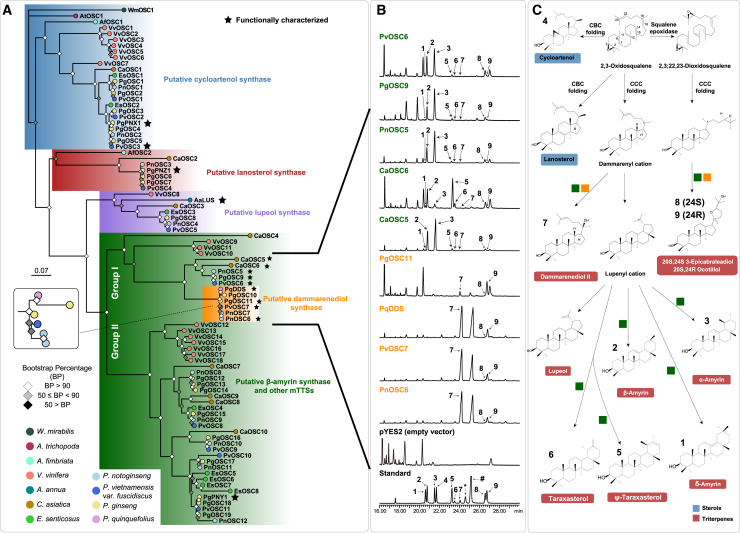
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis and functional characterization of OSCs.
(A) ML phylogenetic tree of OSCs based on codon alignments. Bootstraps are shown as colored squares at each node, and species are shown as colored circles at each terminal branch.
(B) Functional characterization of nine OSCs using heterologous expression. The asterisk (∗) and hash (#) in the total ion chromatograms (TICs) represent the epoxydammaranes mono-trimethylsilyl ether and dammarenediol-II mono-trimethylsilyl ether, respectively. 1, δ-amyrin; 2, β-amyrin; 3, α-amyrin; 4, cycloartenol; 5, ψ-taraxasterol; 6, taraxasterol; 7, dammarenediol-II; 8, 20S,24S-3-epicabraleadiol; 9, 20S,24R-ocotillol.
(C) Schematic for triterpenoid biosynthesis with sterols highlighted in blue and triterpenes highlighted in red. Compound numbers correspond to the numbers in TICs from (B). Colored squares indicate functions of enzymes in (B).