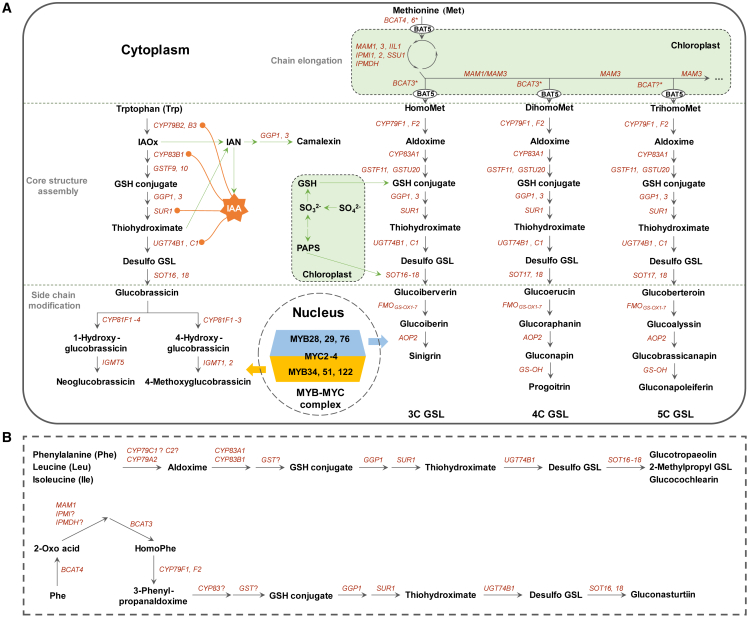
Figure 1.
De novo biosynthetic pathways of GSLs in A. thaliana.
(A)De novo biosynthesis of Met-derived aliphatic GSLs and Trp-derived indole GSLs. BCAT3 is a chloroplast enzyme that has a specific role in the production of homoMet and dihomoMet. BCAT4 and BCAT6 are both cytosolic enzymes. Catalyzed by MAMs, chain-elongated 2-keto acids can be transaminated either in chloroplasts by BCAT3 or by BCAT4/BCAT6 following export by BAT5 from the chloroplasts to the cytoplasm. This transport process is not shown in Figure 1. The negative feedback loops between IAA and GSL biosynthetic genes are indicated by orange lines. The camalexin biosynthetic pathway that intersects with GSL biosynthesis intermediates is indicated by green arrows. GSH, glutathione; PAPS, 3′-phosphoadenosine-5′-phosphosulfate; IAOx, indole-3-acetaldoxime; IAN, indole-3-acetonitrile.
(B) The proposed biosynthetic pathways of Phe-derived glucotropaeolin, Leu-derived 2-methylpropyl GSL, and Ile-derived glucocochlearin (upper), as well as homoPhe-derived gluconasturtiin (lower). The involvement and function of genes that are followed by a question mark (“?”) remain to be investigated in A. thaliana.
Information sources: Hull et al. (2000); Mikkelsen et al. (2000, 2004); Bak et al. (2001); Bak and Feyereisen (2001); Reintanz et al. (2001); Chen et al. (2003); Naur et al. (2003); Grubb et al. (2004, 2014); Schuster et al. (2006); Knill et al. (2008); Sønderby et al. (2010b); Geu-Flores et al. (2011); Lächler et al. (2015); Liu et al. (2016b); Petersen et al. (2019); Harun et al. (2020); Wang et al. (2020); Shang et al. (2022).