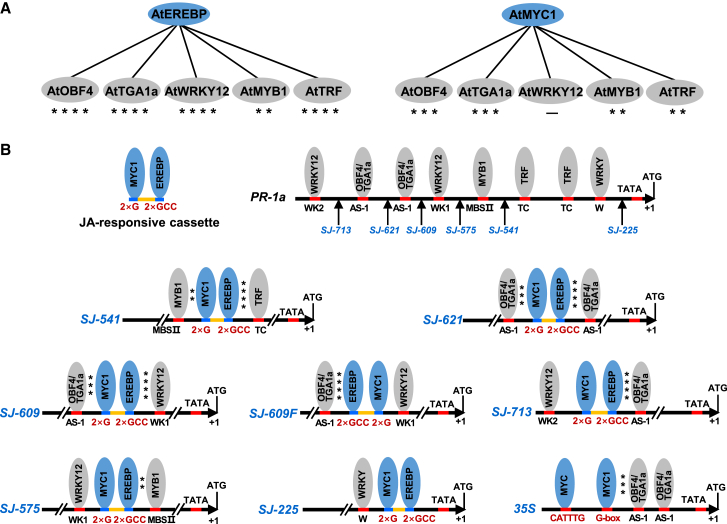
Figure 1.
Schematic representations of synthetic promoters that respond to SA and JA signals.
(A) Interactions between SA- and JA-responsive trans-acting factors. Interaction strength was estimated by the intensity of YFP fluorescence (Supplemental Figure 4).
(B) Schematic representations of PR-1a, 35S, and synthetic promoters constructed in this study. The JA-responsive cassette contains two G-box (2×G) and two GCC-box (2×GCC) elements with a 29-bp spacer sequence from the NtPMT promoter. MYC1 and EREBP are JA-responsive trans-acting factors that can bind to G- and GCC-boxes in the promoter sequences, respectively. The sequence of the JA-responsive cassette is shown in Supplemental Figure 3. The insertion site of the JA-responsive cassette in PR-1a is indicated by arrows. Numbers indicate the positions of the insertion sites relative to the start codon (ATG). WRKY12, OBF4/TGA1a, MYB1, and TRF are SA-responsive trans factors that can bind to WK1/WK2, AS-1, MBSII, and TC-rich repeats in the promoter sequences, respectively. TATA is the TATA box. ∗∗∗∗More than 10 fluorescent spots per 0.1 mm2, ∗∗∗five to 10 fluorescent spots per 0.1 mm2, ∗∗two to five fluorescent spots per 0.1 mm2, ∗one fluorescent spot per 0.1 mm2, superscript minus sign (−) indicates no fluorescence signal. 35S is the CaMV 35S promoter.