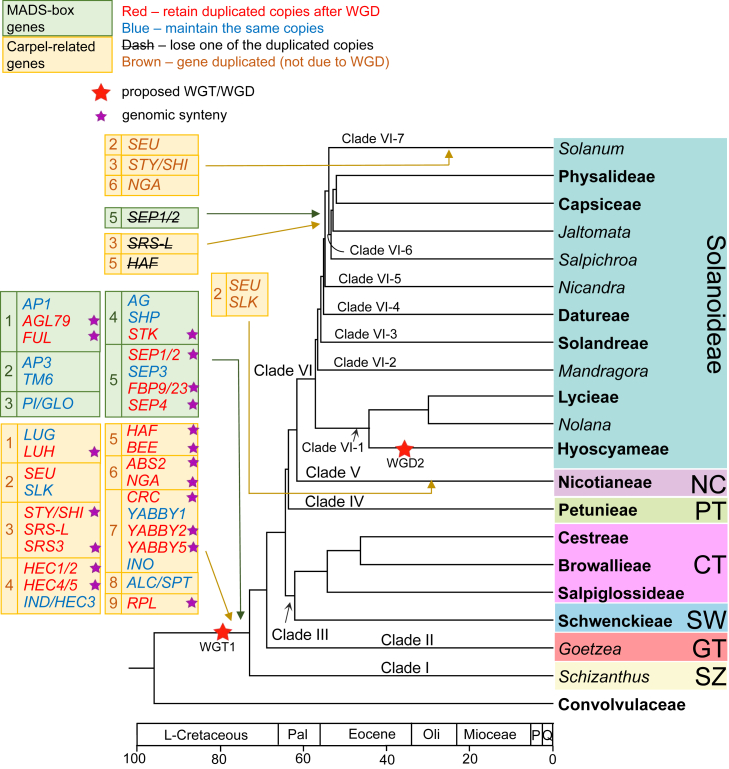
Figure 5.
An overview of evolutionary histories of genes related to carpel and fruit development in Solanaceae.
A simplified Solanaceae phylogenetic tree shows retained duplicates or losses after WGDs. Genes in the rectangle with light green backgrounds are MADS-box transcription factors, and those with yellow backgrounds are carpel developmental control genes. Genes from the same gene (sub)family are in a rectangular frame labeled with numbers. Numbers in the MADS-box genes (light green background) indicate these five subfamilies: 1 (AP1), 2 (AP3), 3 (PI), 4 (AG), 5 (SEP); numbers in the carpel-related genes (yellow background) indicate the following nine gene families: 1 (LUG-like), 2 (SEU-like), 3 (STY/SHI/SRS-like), 4 (HEC/IND-like), 5 (HAF-like), 6 (RAV/NGA-like), 7 (YABBY-like), 8 (ALC), and 9 (RPL). Red letters represent retention of duplicated copies after WGD; letters with a dash indicate retention of duplicated copies after WGD but later loss of one gene copy; blue letters indicate maintenance of the same copy number; and brown letters indicate other gene duplication (not due to WGD). Red stars indicate the WGT/WGD events proposed here. Purple stars represent duplicated copies with collinearity support in model plants (C. annuum, N. tabacum, P. axillaris, P. inflata, and/or S. lycopersicum). Tip labels of the phylogenetic tree indicate the genus (italic) or tribe (bold). Tribes and subfamilies are highlighted with different colors, with their names shown on the right. SZ, Schizanthoideae; GT, Goetzeoideae; SW, Schwenckioideae; CT, Cestroideae; PT, Petunioideae; NC, Nicotianoideae. Branch lengths of the tree are proportional to ages.