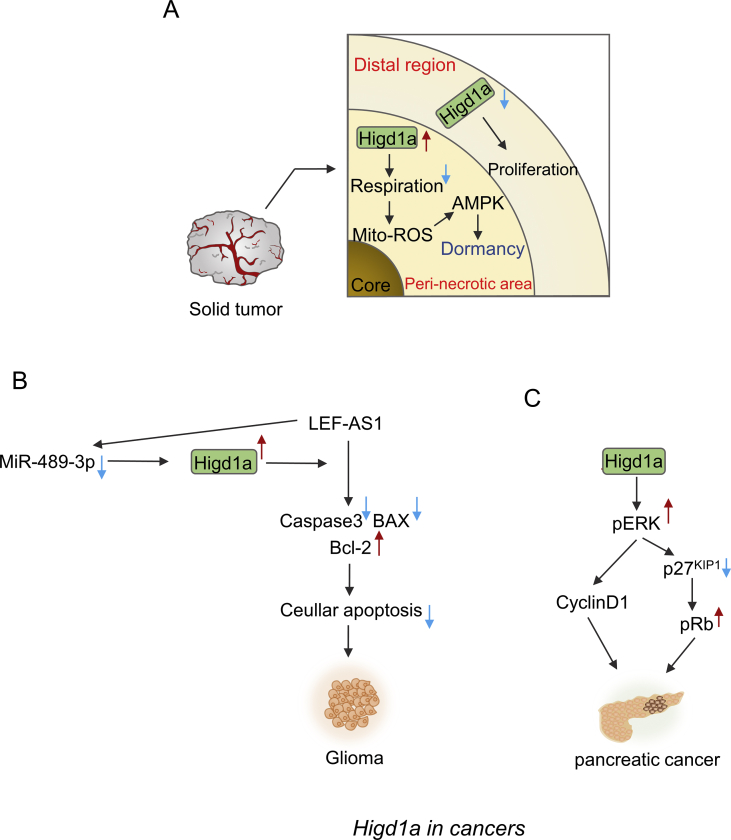
Figure 5.
Diverse roles of Higd1a in cancers. (A) In the peri-necrotic area of some solid tumors, where serious hypoxia and poor vascularity occur, Higd1a expression is elevated, which is owing to decreased expression of DNMT1 that leads to the decreased DNA methylation on Higd1a promoter. In this area, Higd1a inhibits mitochondrial respiration of the tumor cells, which will elevate mitochondrial superoxide (O2−) to activate AMPK pathway for adaptive response. Activation of AMPK pathway will attenuate oxidative stress and finally bring about dormancy of tumor cells. In this way, Higd1a hijacks the tumors to deter further development of cancers and keeps them in dormancy. In contrast, in the distal region to necrosis with mild to moderate hypoxia, Higd1a expression is inhibited as a result of up-regulation of DNMT1. In this area, Higd1a functions as suppressor for the growth of tumor cells. Cancer cell shows a rapid growth when Higd1a expression level is repressed in this area. (B, C) However, in some other cases, Higd1a has the ability to expedite the proliferation of tumor cells. (B) In glioma, miR-489-3p can bind to the mRNA of Higd1a to inhibit Higd1a expression, while LEF1-AS1 can bind to miR-489-3p to block the inhibitory effect of miR-489-3p on Higd1a expression. Higd1a could facilitate LEF1-AS1-mediated inhibition of apoptosis as indicated by the decrease of cleaved caspase 3 and Bax expression, along with the increase of Bcl-2 expression, which will promote the growth of glioma. (C) In pancreatic cancer cells, Higd1a will increase ERK activity, thereby decreasing the expression of p27KIP1 and increasing the expression of cyclin D1. Moreover, decreased p27KIP1 boosts phosphorylation of Rb protein to repress the function of Rb protein. The effects above will ultimately promote the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells.