Figure 1.
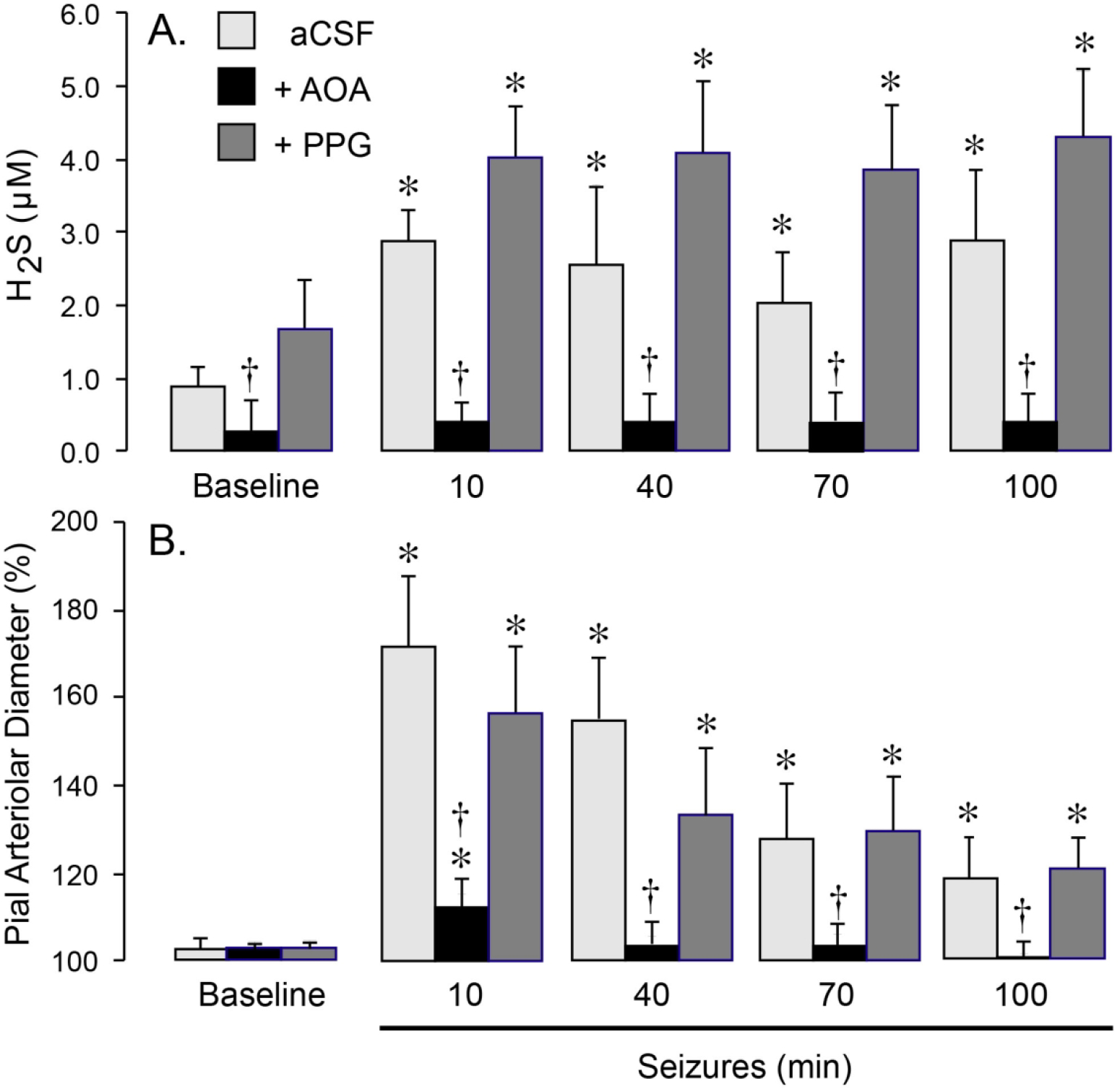
CBS contributes to brain H2S production (A) and pial arteriolar dilation (B) during seizures. Seizures were induced by bicuculline (3 mg/kg, i.p.) in newborn pigs, that were untreated (aCSF) or treated with selective inhibitors of CBS (AOA, 5 mM) or CSE (PPG, 5 mM) that were topically applied to the cortical surface. A: H2S concentrations in periarachnoid cerebrospinal fluid (pCSF) collected from the closed cranial windows in 10-m intervals before (Baseline) and 10–100 m after bicuculline administration. B: Dilator responses of pial arterioles to seizures 10–100 m after bicuculline administration. N = 6 pigs per group. Values are means ± SD. *P < 0.05, compared with the corresponding baseline values. †P < 0.05, compared with the corresponding values in untreated pigs.
