Figure 4.
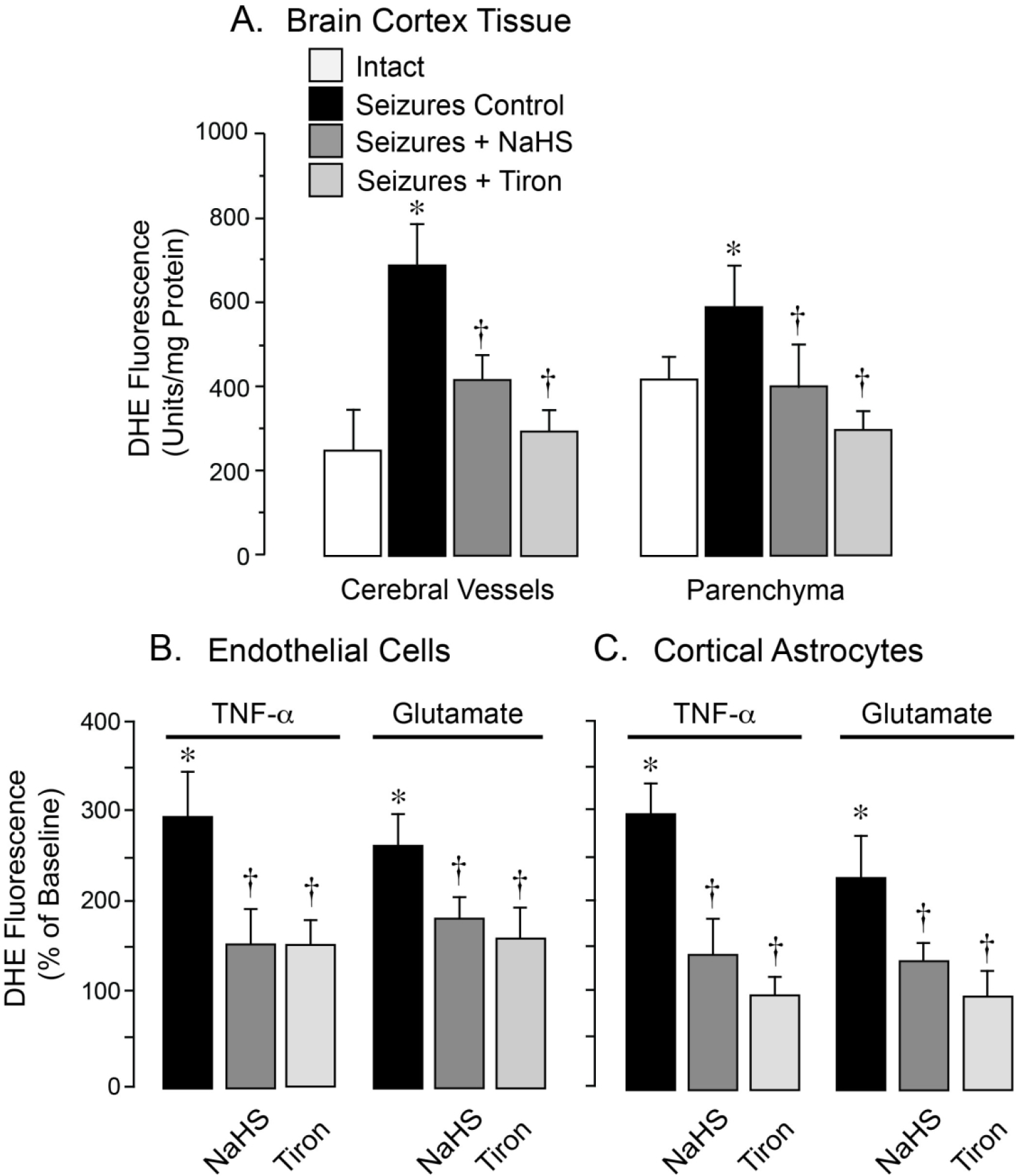
Antioxidant effects of NaHS in the epileptic brain (A) and in cultured neurovascular cells exposed to seizure-related pro-oxidants (B, C). ROS production was evaluated by the fluorescent products of DHE oxidation. A: Seizures were induced by bicuculline (3 mg/kg, i.p.) in untreated newborn pigs (Seizures Control) and in pigs pretreated with NaHS (3 mg/kg, i.p.) or the superoxide scavenger Tiron (2 g/kg, i.v.) Cerebral vessels and astrocyte-enriched brain cortex parenchyma were isolated 1 h after bicuculline administration (N = 4 animals per group). B, C: Primary cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (B) and cortical astrocytes (C) were treated for 1 h with pro-oxidants TNF-α (30 ng/ml) or glutamate (2 mM) in the absence or presence of NaHS (20 μM) or Tiron (1 mM). Values are means ± SD. *P < 0.05 compared with intact values. †P < 0.05 compared with seizure control values (A) or with TNF-α or glutamate alone (B, C).
