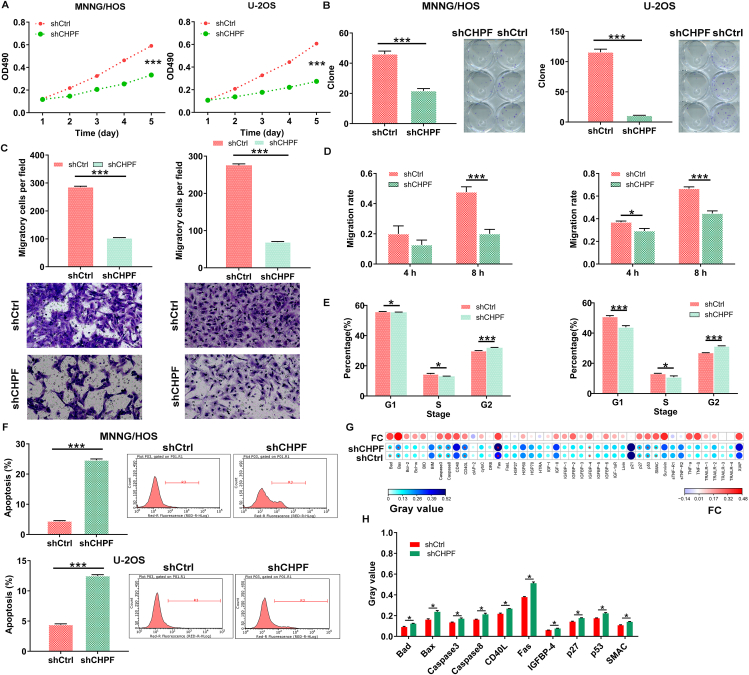
Figure 2.
CHPF knockdown inhibited cell proliferation, colony formation and migration, induced cell apoptosis. (A) MTT assay was used to detect the effects of CHPF knockdown on cell proliferation of MNNG/HOS and U-2OS cells. (B) The abilities of MNNG/HOS and U-2OS cells to form colony after infection were assessed. (C, D) The effects of CHPF knockdown on MNNG/HOS and U-2OS cell migration capacities were detected by Transwell assay (C) and wound-healing assay (D). (E, F) Flow cytometry was performed to evaluate the effects of CHPF knockdown on cell cycle (E) and apoptosis (F) of MNNG/HOS and U-2OS cells. (G, H) The changes in apoptosis-related proteins were analyzed in MNNG/HOS cells following infection by a Human Apoptosis Antibody Array. Protein level was visualized by R studio (G) and presented in gray value (H). The data were expressed as mean ± SD. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001.