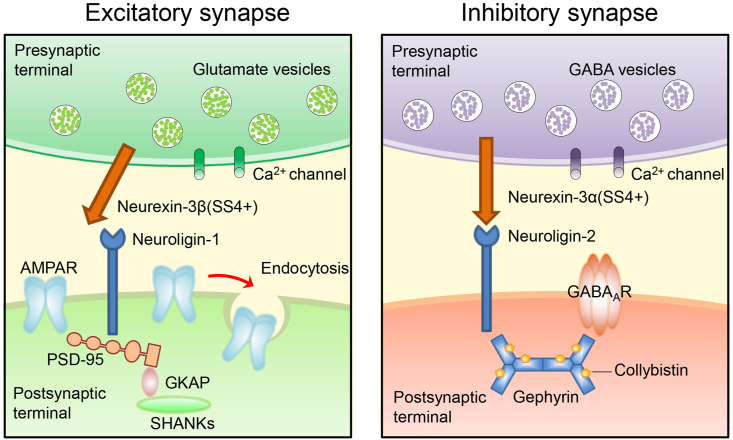
Figure 3.
Two signaling pathways reported based on synaptic junctions formed by neurexin-3 that alter synaptic function. To date, the complete signaling pathway responsible for the change in synaptic function in response to the expression of neurexin-3 has not been fully explained; however, the association of neurexin-3 with AMPARs and GABAARs signaling pathways has been observed. At excitatory synapses, by blocking neuroligin-1 pairing, neurexin-3β (SS4+) prevents postsynaptic density-95 (PSD-95) from recruiting specific postsynaptic proteins that are present in glutamate synapses, including AMPARs. PSD-95 binds to guanylate kinase-associated protein (GKAP), which is an adaptor protein, and GKAP binds to SHANKs. Moreover, neurexin-3β (SS4+) promotes the endocytosis of AMPARs in the postsynaptic membrane. At inhibitory synapses, neurexin-3α (SS4+) interacts with neuroligin-2 and specifically activates collybistin. Neuroligin-2 and activated collybistin are involved in the recruitment of gephyrin, which then recruits GABAARs to the postsynaptic membrane. In addition, neurexin-3α located in the presynaptic membrane acts directly on postsynaptic GABAARs.