Figure 2.
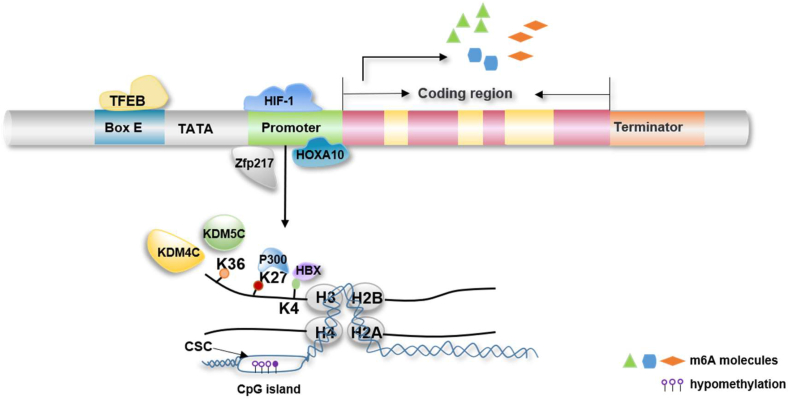
Transcription-level regulation of m6A molecules. The transcription level of m6A molecules is mainly regulated by two aspects: 1. Activation of transcription factors. The transcription factor TFEB can bind to the conserved E-box in the promoter to promote ALKBH5 expression. Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) directly binds to the ALKBH5 promoter and promotes its transcription, HOXA10 promotes ALKBH5 transcription by binding to the ALKBH5 promoter, and Zfp217 binds to the FTO promoter to activate its transcription. 2. Histone modification. The histone demethylase KDM4C regulates ALKBH5 transcription by modifying histone H3K36me3 in the ALKBH5 promoter. HBX mediates the modification of K3K4me3 in the ALKBH5 promoter to promote ALKBH5 transcription, and KDM5C promotes its transcription through demethylated METTL14 histone H3K36me3 modification. P300 regulates METTL3 transcription by mediating the acetylation of METTL3 histone K27. Cigarette smoke condensate (CSC) causes hypomethylation of METTL3 and ALKBH5 CpG islands and regulates their transcription level.