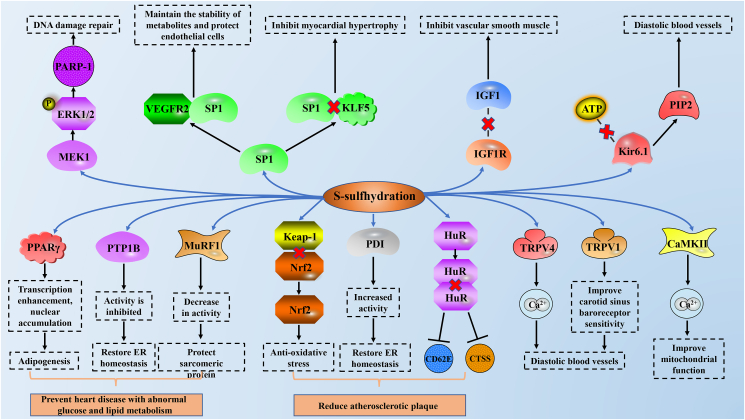
Figure 2.
The role of different proteins in the cardiovascular system after S-sulfhydration. After protein S-sulfhydration, it exerts anti-oxidative stress in the cardiovascular system, restores ER homeostasis, regulates ion channels, and regulates glucose and lipid metabolism. It plays a role in blood pressure regulation, atherosclerotic plaque formation, and cardiac hypertrophy. CaMKII: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II; CTSS: cathepsin S; ER: endoplasmic reticulum; ERK1/2: extracellular regulated protein kinase 1/2; HuR: human antigen R; IGF1: insulin-like growth factor-1; IGF1R: insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor; Keap-1: Kelch-like ECH-associated protein1; Kir6.1: ATP-sensitive potassium channel 6.1; KLF5: Krüppel-like factor 5; MEK1: mitogen-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1; MuRF1: muscle RING finger-1; Nrf2: nuclear factor E2-related factor 2; PARP-1: poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase-1; PDI: protein disulphide isomerase; PIP2: phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate; PPARγ:peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ; PTP1B: protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B; SP1: specific protein-1; TRPV4 and TRPV1: transient receptor potential family member; VEGFR2: vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2.