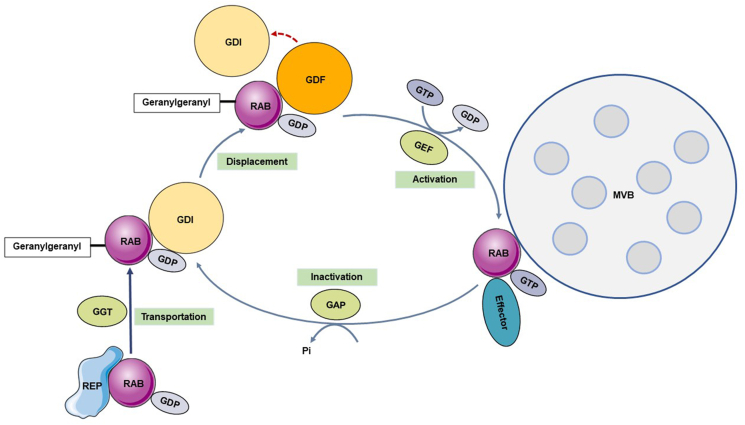
Figure 2.
The RAB switch and its dynamic cycling model. The newly synthesized RAB in the cytoplasm is captured by RAB escort protein (REP) in a GDP-bound inactive form and transported to RAB geranylgeranyl transferase (RGGTase). Here, hydrophobic geranylgeranyl groups are added, allowing RAB to reversibly bind to the target membrane. GDP dissociation inhibitor (GDI) recognizes and binds to the inactivated form of RAB protein to stably store RAB in the cytoplasm. Upon activation, GDI displacement factors (GDFs) help RAB dissociate from GDI so that it can bind to the target membrane. Meanwhile, GDP is replaced with GTP by guanine nucleotide exchange factors (GEFs), which then activate RAB protein attached to the target membrane. After this step is completed, RAB recruits GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) to hydrolyze GTP and convert the protein to an inactive form.