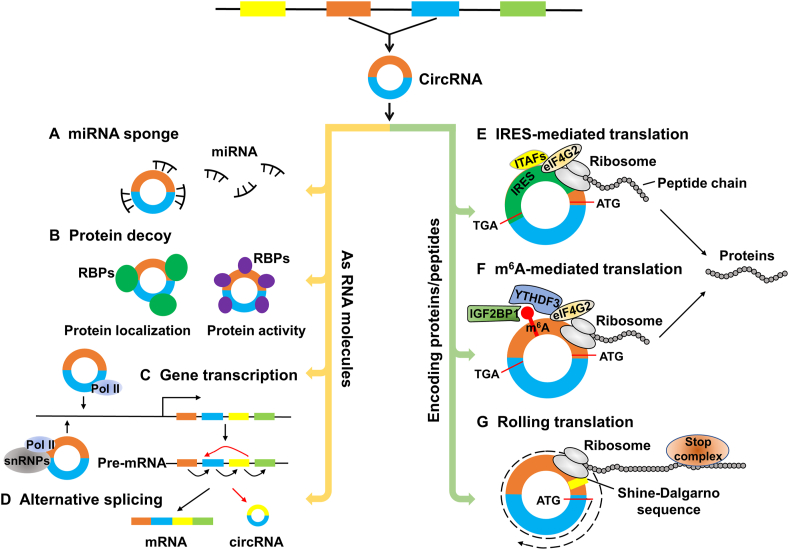
Figure 1.
The functions and translation mechanisms of circRNAs. (A–D) circRNAs, as RNA molecules, regulate miRNA functions as miRNA sponge (A), protein localization and activity as protein decoy (B), gene transcription (C), and alternative splicing (D). (E–G) circRNAs exert their functions by encoding proteins or peptides through cap-independent mechanisms. (E) IRES-mediated translation. eIF4G2 recognizes and bonds IRES on circRNA to recruit ribosomes and initiate translation with the assistance of IRES-transacting factors (ITAFs). (F) m6A-mediated translation. YTH domain family protein 3 (YTHDF3) or insulin-like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 1 (IGF2BP1) recognizes m6A modified circRNA and recruits eIF4G2 to m6A to initiate the translation. (G) Rolling translation. CircRNA containing an infinite ORF and start codon (ATG) enables continuous translation. The ribosomal-binding Shine–Dalgarno (SD) sequence on circRNA is associated with the rolling translation initiation, and a stop complex system named “programmed-1 ribosomal frameshifting (-1PRF)-mediated out-of-frame stop codon” can terminate rolling translation in certain natural circRNAs. IRES, internal ribosome entry sites; m6A, N6-methyladenosine; RBPs, RNA-binding proteins; Pol II, polymerase II; snRNP, small nuclear ribonucleoprotein.