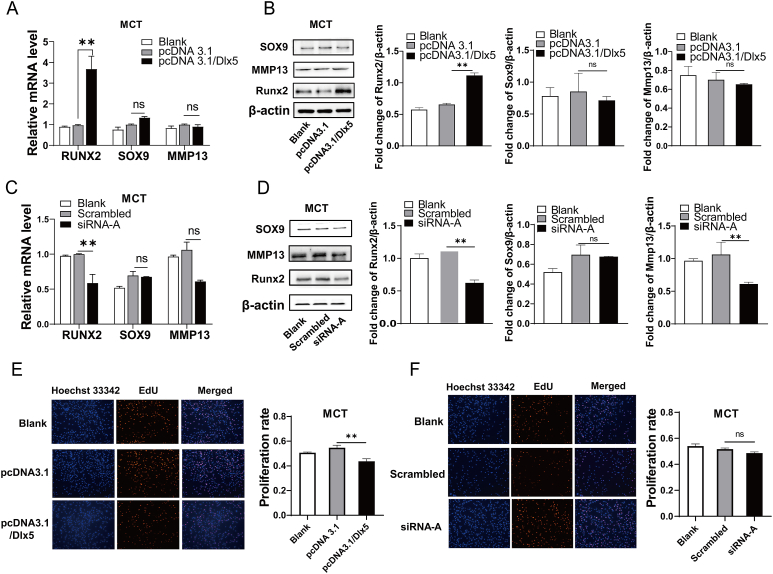
Figure 7.
Effects of DLX5 on chondrocyte differentiation and proliferation. (A) The mRNA levels of Runx2, Sox9, and Mmp13 were detected by qRT-PCR after MCT cells were transiently transfected with pcDNA3.1/Dlx5 for 24 h respectively. (B) Western blotting analysis was used to examine the protein levels of RUNX2, SOX9, and MMP13 in MCT cells transiently transfected with pcDNA3.1/Dlx5 for 48 h respectively. β-actin was used as an internal control. (C) The mRNA levels of Runx2, Sox9, and Mmp13 were detected by qRT-PCR after MCT cells were transiently transfected with Dlx5 siRNA-A for 24 h. (D) Western blotting analysis was used to examine the protein levels of RUNX2, SOX9, and MMP13 in MCT cells transiently transfected with Dlx5 siRNA-A for 48 h. β-actin was used as an internal control. (E) MCT cells were transfected with pcDNA3.1/Dlx5 and pcDNA3.1 for 48 h, and EdU assays were performed to detect cell proliferation ability. (F) MCT cell proliferation ability was detected by EdU after MCT cells were transfected with Dlx5 siRNA-A and scrambled sequences. The results showed that the Runx2 was significantly increased in Dlx5-treated cells, while no significant change in levels of Sox9 and Mmp13 expression. Dlx5 over-expression suppressed MCT cell proliferation, but the knockdown of Dlx5 had no obvious effect on chondrocyte proliferation. Data were expressed as mean ± SEM from three independent experiments. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01.