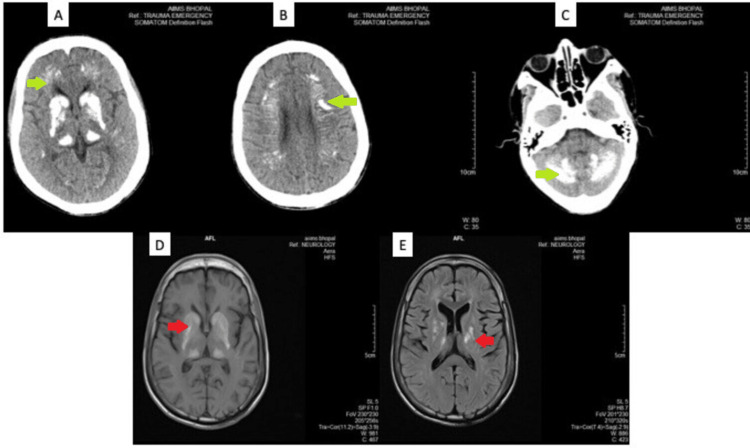
Figure 1. Non-contrast CT and MRI images showing symmetrical areas of bilateral intracranial calcification.
(A)-(C) are NCCT images showing symmetrical areas of calcification (green arrows) in bilateral basal ganglia and thalami, head of caudate nucleus, lentiform nucleus, and thalamus (A), periventricular white matter (B), and cerebellar hemispheres (C). (D) and (E) are corresponding MRI images showing symmetrical areas of altered signal intensity (red arrows) involving bilateral basal ganglia, thalami, periventricular and deep white matter, corona radiata, centrum semiovale (D). There also are multiple small confluent areas of gliosis in bilateral centrum semiovale, suggestive of old infarcts (E).