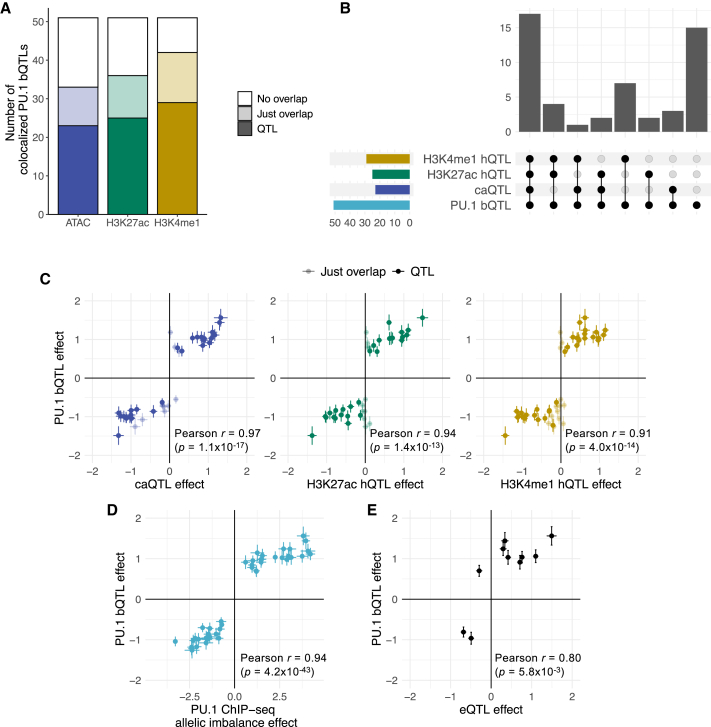
Figure 4.
Regulatory effects of the colocalized PU.1 motif-altering variants
(A) Number of colocalized PU.1 motif-altering variants that overlap ATAC-seq or histone mark (H3K27ac or H3K4me1) ChIP-seq peaks and that are in LD (r2 > 0.8) with those regulatory QTLs.
(B) Upset plot showing the number of colocalized PU.1 motif-altering variants that are in LD (r2 > 0.8) with different sets of regulatory QTLs. caQTL, chromatin accessibility QTL; hQTL, histone QTL.
(C) Comparison of PU.1 bQTL effects (i.e., regression effect size) with other regulatory QTL effects. Each point corresponds to a PU.1 motif-altering variant. The colors match those in (A). The error bars represent standard errors. Pearson correlation coefficient is calculated only for those points showing significant regulatory QTLs.
(D) Comparison of PU.1 bQTL effects and PU.1 ChIP-seq allelic imbalance effect (i.e., log2[allelic fold change] estimated from weighted linear regression). The effect is with respect to the alternate alleles. The error bars represent standard errors.
(E) Comparison of PU.1 bQTL effects with eQTL effects. Each point corresponds to a PU.1 motif-altering variant. For rs3808619, which had multiple eQTL signals, only the value for the closest gene, ZC2HC1A, is shown. The error bars represent standard errors.
See also Tables S10, S11, S12, S13, and S14.