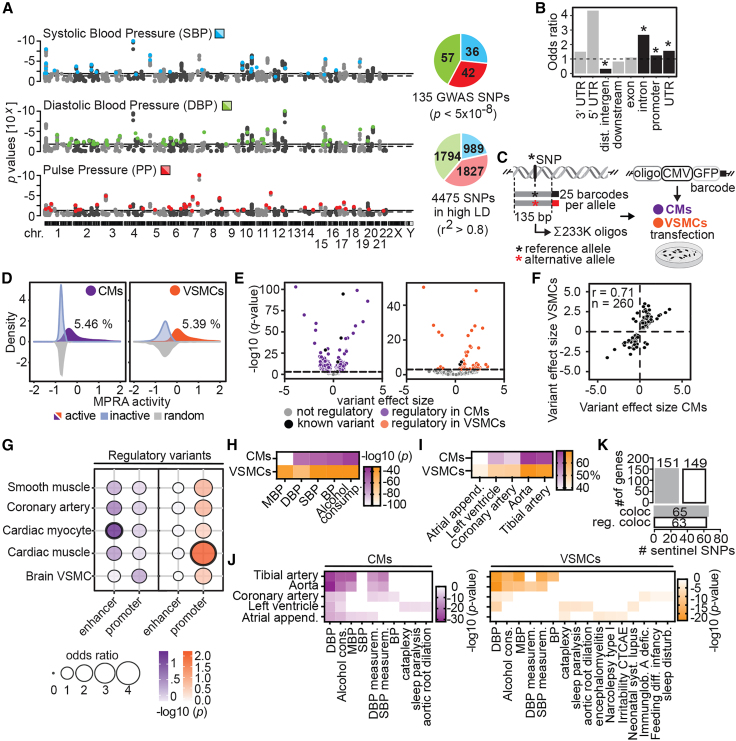
Figure 1.
Functional characterization of genetic variants associated with blood pressure
(A) Genomic location of GWAS sentinel variants (colored, p < 5 × 10−8) and variants in high LD (gray, ±500 kb, r2 > 0.8) for each of the blood pressure traits.
(B) Enrichment of GWAS variants at DNA and RNA regulatory elements using ChIPseeker.37 Bars above odds ratio >1 (dotted line) denote enrichment, with black bars indicating significance (∗adjusted p < 0.05), while odds ratios <1 denote depletion. Downstream, gene end (<3 kb); dist., distal.
(C) MPRA design. Each reference and alternative allele (centered in 135 bp elements) was linked to 25 unique barcodes and cloned in front of a minimal CMV promoter and GFP reporter. Differentiated cardiomyocytes (CMs) and vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) were transfected with the plasmid pool and barcodes were quantified.
(D) MPRA activity distribution of active sequences for CMs (5.46%) and VSMCs (5.39%).
(E) Variant effect sizes (log2 fold change) of reference allele activity vs. alternative allele in CMs (left) and VSMCs (right). Variants with significant regulatory activities are colored. Log2 fold change >0 indicates higher activity for reference sequence, while <0 indicates more activity of the alternative sequence.
(F) Effect size correlation between regulatory variants in CMs and VSMCs. Spearman’s rho (r) and number of sequences (n) are shown.
(G) Enrichment of regulatory elements at enhancer and promoter elements in five tissues. Thick black outlines represent significance at adjusted p < 0.05.
(H) Functional enrichment analysis of regulatory variants nearest neighboring genes. MBP, mean blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; SBP, systolic blood pressure.
(I) Regulatory variants overlap GTEx eQTLs in BP-related tissues, especially in aorta and tibial artery.
(J) Functional enrichment analysis of nearest-neighbor genes of regulatory variants overlapping eQTLs.
(K) Colocalization analysis of regulatory variants. Upper bar plot shows the number of eGenes (target gene of an eQTL) colocalized with all analyzed BP GWAS loci (coloc) and GWAS loci with at least one regulatory variant in LD (reg. coloc). Bottom bar plot shows the number of all analyzed BP GWAS loci and GWAS loci with at least one regulatory variant in LD that colocalizes with eQTLs. Only eQTLs defined in GTEx cardiovascular-related tissues are shown. See also Figures S1 and S2; Tables S1, S2, S3, and S4.