Figure 6.
Polygenic risk for lipodystrophy-like phenotype manifests in cellular programs that indicate increased mitochondrial activity, reduced actin cytoskeleton remodeling, and reduced lipid accumulation capacity in subcutaneous adipocytes
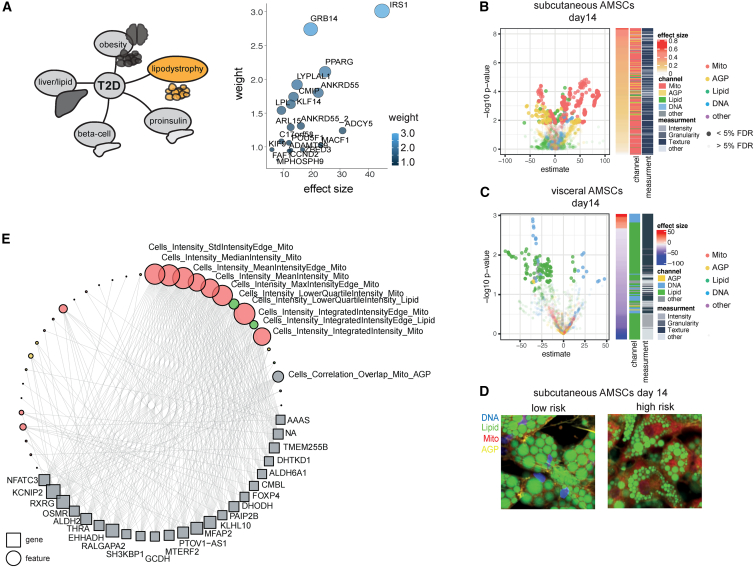
(A) Schematic of T2D process-specific PRS (left panel). Lipodystrophy-specific PRS consists of 20 T2D-associated loci contributing to polygenic risk for a lipodystrophy-like phenotype.59 y axis: weights of individual loci; x axis: effect size of individual loci contributing to polygenic risk for a lipodystrophy-like phenotype.
(B–D) Depot-specific effects on LipocyteProfiles in AMSCs at day 14 are under the polygenic control of the lipodystrophy cluster with a mitochondrial and AGP-driven profile in subcutaneous AMSCs (B), whereas in visceral AMSCs mostly Lipid features were associated with increased polygenic risk (C). See also Figure S6A (days 0, 3, and 8). Computationally averaged images of subcutaneous AMSCs from low- and high-risk allele carriers for lipodystrophy PRS show higher mitochondrial intensity, reduced cortical actin, and reduced lipid-droplet size in high-risk carriers (D).
(E) Gene-feature connections for lipodystrophy PRS-mediated differential features are enriched for Mitochondrial Intensity features informative for mitochondrial membrane potential in subcutaneous AMSCs at day 14 (FDR < 0.1%). See also Figure S6D.