Figure 3.
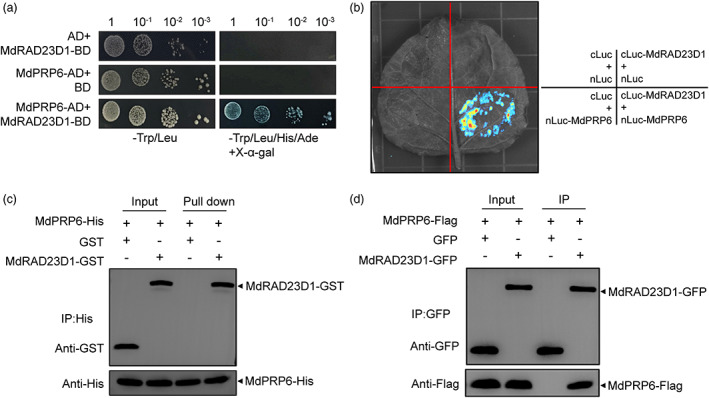
MdRAD23D1 interacts with MdPRP6 in vivo and in vitro. (a) Yeast two‐hybrid assays. The full‐length CDS of MdRAD23D1 and MdPRP6 were cloned into pGBKT7 and pGADT7 vectors, respectively. Co‐transformed yeast cells were grown on SD‐Trp/‐Leu and SD‐Trp/‐Leu/‐His/‐Ade+X‐α‐gal medium. (b) The Split‐Luc assay. The full‐length CDS of MdRAD23D1 and MdPRP6 were cloned into pRI‐101‐cLuc and pRI‐101‐nLuc, respectively. The fusion proteins MdRAD23D1‐cLuc and MdPRP6‐nLuc were transiently co‐expressed in Nicotiana benthamiana leaves, and the fluorescence signal was observed by an Ultra‐sensitive multifunctional imager (Uvitec). (c) Pull‐down assays. Escherichia coli–expressed MdPRP6‐His protein was first incubated with anti‐His magnetic beads and then the mixture was incubated with E. coli‐expressed GST or MdRAD23D1‐GST. The bound proteins were eluted and detected using anti‐GST and anti‐His antibodies. (d) Co‐IP assay. The fusion proteins MdRAD23D1‐GFP and MdPRP6‐Flag were transiently co‐expressed in N. benthamiana leaves, and the total proteins were extracted and immunoprecipitated with anti‐GFP magnetic beads. Immunoblotting was performed with anti‐GFP and anti‐Flag antibodies.
