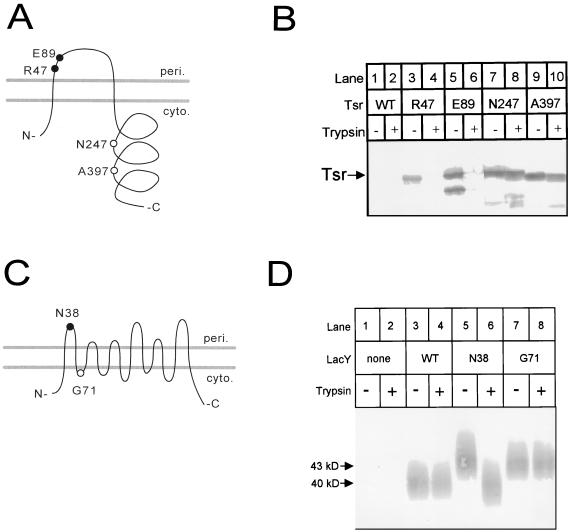
FIG. 1.
Trypsin cleavage of insertion derivatives of lac permease and Tsr. (A) Positions in the Tsr topology of the 31-residue insertions examined. Closed circles denote trypsin sensitivity in spheroplasts, and open circles denote trypsin resistance. The alkaline phosphatase activities of cells expressing the tsr-ISphoA/in insertions used to generate the 31-residue insertions indicated were measured for plasmids in strain CC118. The alkaline phosphatase activities (expressed in activity units ± standard deviation) were as follows: no plasmid, 1.7 ± 0.1; R47, 2162 ± 49; E89, 2589 ± 22; N247, 14 ± 1; and A397, 8 ± 0.4. peri., periplasmic; cyto., cytoplasmic. (B) Western blot of Tsr insertion derivatives following trypsin treatment of spheroplasts. A polyclonal antiserum directed against the inserted sequence was used to develop the blot (25). The trypsin treatment led to the production of polypeptides approximately the sizes expected for N-terminal fragments resulting from cleavage within the two periplasmic inserts (∼6.5 kDa for R47 and ∼15 kDa for E89) (not shown). Trypsin treatment procedure 2 with cells grown at 30°C was used. (C) Positions in the lac permease topology of the N38 and G71 31-residue insertions. The closed circle indicates trypsin sensitivity in spheroplasts; the open circle indicates resistance. (D) Western blot of lac permease insertion derivatives following trypsin treatment of spheroplasts. A polyclonal antiserum directed against the C terminus of lactose permease was used to develop the blot. lac permease runs as a broad band in SDS-PAGE. Strain CC874 carrying different plasmids was analyzed by trypsin treatment procedure 1 with cells grown at 37°C. WT, wild type.