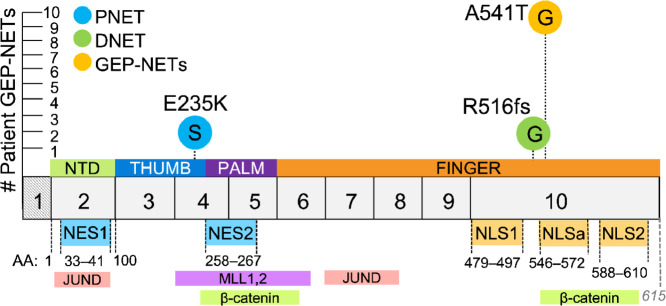
FIGURE 1.
WES of patient-derived GEP-NETs identifies germline and somatic mutations in the human MEN1 gene. Germline and somatic MEN1 mutations and variants were previously identified by WES of matched buffy coat and tumor specimens from 9 patients with clinically confirmed GEP-NETs (20). A 10th patient was included in the study analysis following clinical testing for MEN1. We focused our investigation on three single-nucleotide mutations: a c.1546dupC germline mutation identified in a duodenal NET (DNET) that results in a frameshift mutation and introduction of an arginine at amino acid (aa) 516 (R516fs); a c.703G>A somatic mutation identified in a PNET resulting in a glutamic acid to lysine substitution at aa 235 (E235K); and a c.1621G>A germline polymorphism identified in all nine patient samples that underwent WES. In this patient cohort, the c.1621G>A polymorphism results in an alanine to threonine substitution at aa 541 (A541T) immediately upstream to an NLSa. Menin has three NLS sequences in exon 10 and two nuclear export signal (NES) sequences. G = germline, S = somatic, aa = amino acid, NES = nuclear export signal, NLS = nuclear localization signal, NTD = N-terminal domain. Exon1 (hatched) is transcribed but not translated.