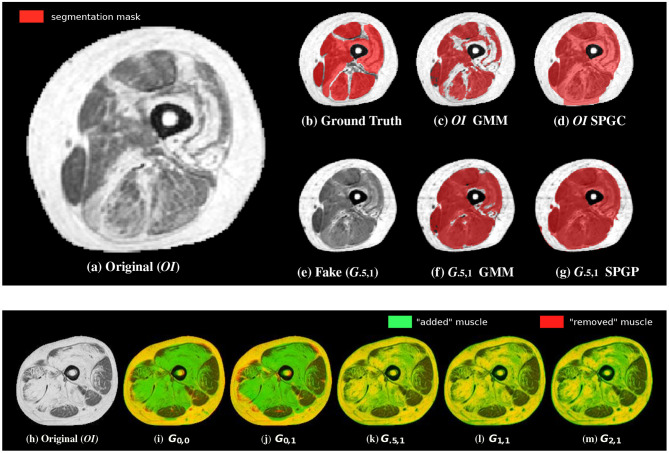
Figure 4.
Example segmentations (c,d) of the original image (a) as well as of the translated images (e–g) in comparison to the ground-truth annotations (b). Although small structures often cannot be completely reconstructed (especially SPGC leads to over-smoothed masks), overall segmentation robustness increases in case of the translated image (f,g). The bottom row shows an overlay of an example original image (h) with the corresponding translated images. Although green color indicates “added” muscle tissue, red color indicates “removed” muscle. Yellow shows unchanged intensities. The configurations without show removed muscle tissue and also added muscle in wrong areas (i,j). This is not the case when including the novel domain specific loss (k–m).