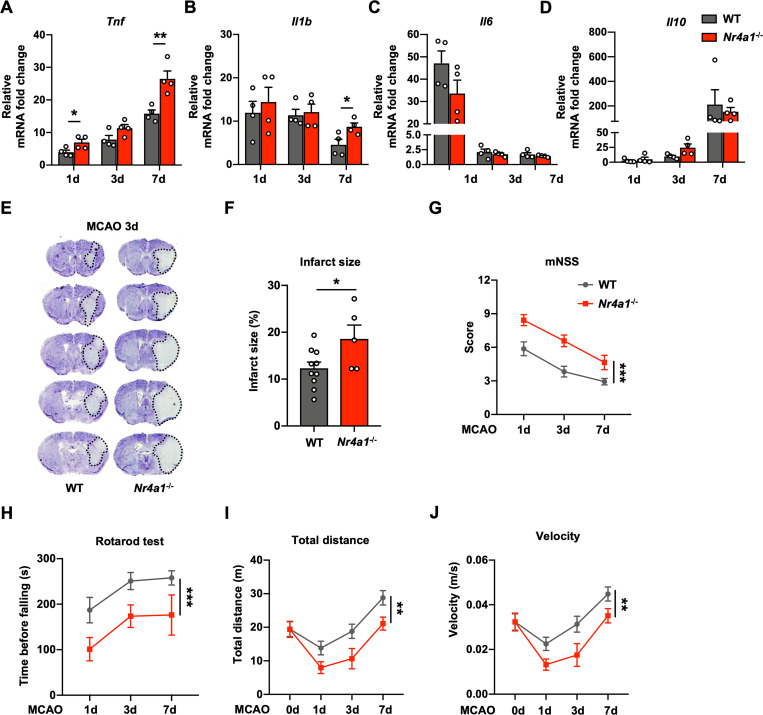
Fig 5. Nr4a1-knockout enhances Tnf expression and exacerbates brain injury in experimental ischemic stroke.
(A–D) Relative mRNA levels of several inflammatory factors in the ipsilateral hemispheres of WT and Nr4a1-/- mice 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days after MCAO compared with those in the contralateral hemispheres (n = 4 mice in each group). (E) Representative images of Nissl staining of tissues from WT and Nr4a1-/- mice 3 days after MCAO. (F) Quantification of the infarct size, as measured by Nissl staining (n = 10 for WT mice, n = 5 for Nr4a1-/- mice). (G–J) Sensorimotor deficits were aggravated in Nr4a1-/- mice compared to WT mice 1 day, 3 days, and 7 days after MCAO, as determined by the mNSS test (G) (n = 15–38 for WT mice, n = 14–28 for Nr4a1-/- mice), rotarod test (H) (n = 14–18 for WT mice, n = 7–16 for Nr4a1-/- mice), total distance traveled (I) (n = 12–30 for WT mice, n = 9–21 for Nr4a1-/- mice), and mean velocity (J) (n = 12–40 for WT mice, n = 9–28 for Nr4a1-/- mice). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. In (A–D) and (F), two-tailed unpaired Student’s t test. In (G–J), two-way ANOVA. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. The underlying data for this figure can be found in S1 Data. MCAO, middle cerebral artery occlusion; WT, wild-type.