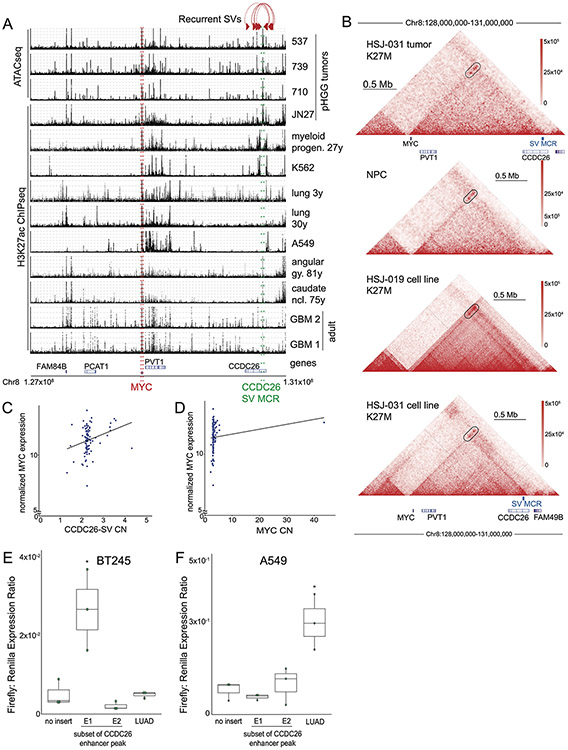
Extended Data Fig. 2. Lineage specificity of the enhancer peak in CCDC26.
(A) ATAC-seq (top) and H3K27ac ChIP-seq (bottom) enrichment (vertical axis) of samples from different lineages (indicated on right; “27y” indicates the sample was obtained from a 27-year-old person) across the TAD encompassing MYC (horizontal axis). The location of the MYC coding sequence is highlighted in red. The CCDC26 amplicon boundaries for the 15 samples with the amplicon are indicated by the paired red arrows at the top. The consensus amplicon is indicated by the green dotted lines and centers on an H3K27ac peak present only in glial samples. (B) Hi-C heatmaps depicting DNA interaction profiles (5 kb resolution) from a midline glioma (top), iPSC-derived neural progenitor cells (2nd from top) and two cell lines harboring H3.3K27M mutations (bottom). Red and white indicate high and low interaction frequencies, respectively. MYC interacts more frequently with the H3K27ac peak within CCDC26 (black oval) relative to neighboring loci. The minimal common region of the CCDC26 amplicon is indicated at the bottom of the heatmaps (SV MCR; blue rectangle). (C-D) Correlation between MYC expression and genomic copy number of (C) its enhancer amplified in the CCDC26-SV (p = 0.01, two-sided Spearman rank correlation test, samples with MYC CN>2.5 excluded, n=94 tumors), or (D) the MYC coding sequence (p = 0.0003, two-sided Spearman rank correlation test, n=114 tumors). (E-F) Lineage specificity of E1 enhancer activity in (E) neural lineage/BT245 p-value(E1vs.Backbone) = 0.0056; p-value(LUAD vs. Backbone) = 0.99 and (F) lung epithelial lineage/A549, p-value(E1 vs. Backbone) = 0.96 ; p-value(LUAD vs. Backbone) = 0.0071, n = 3 independent experiments, Nested One-Way Anova: Tukey’s Multiple Comparisons. Analogous to Fig. 1G; center line of the boxplot indicates the median, bounds of the box the 25th and 75th percentiles and whiskers extend from the box to the largest or smallest value no further than 1.5xIQR.