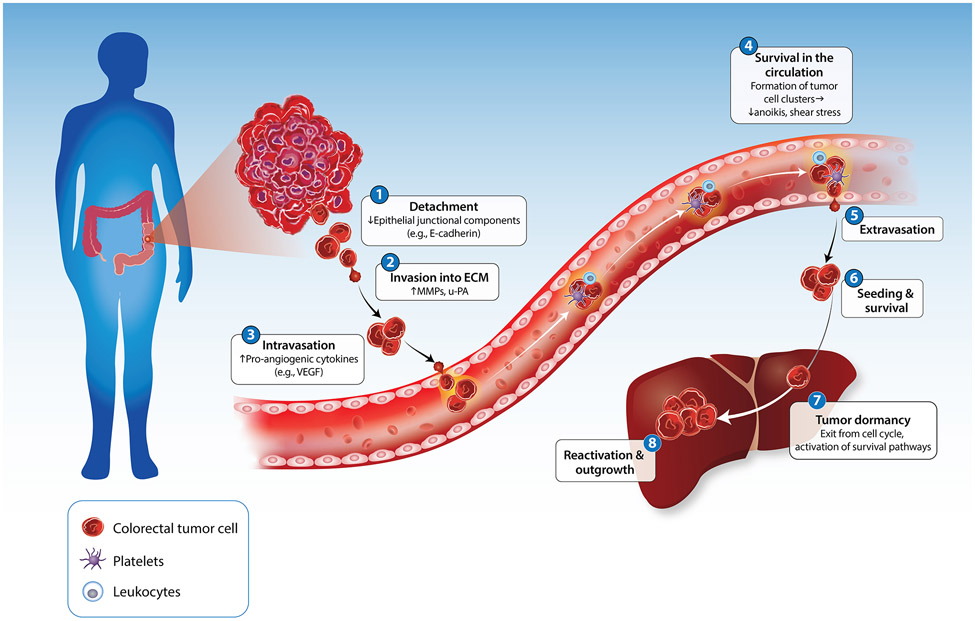
Figure I. The invasion-metastasis cascade in colorectal cancer.
Step 1: tumor cells detach from one another. Step 2: tumor cells invade into the ECM by degrading the basement membrane. Step 3: tumor cells induce angiogenesis and enter the circulation. Step 4: tumor cells survive within the circulation by clustering with each other, leukocytes, and platelets. Step 5: tumor cells that have survived the circulation exit the bloodstream into the stroma of the target organ. Step 6: tumor cells seed into the secondary site. Step 7: tumor cells enter a dormant state, characterized by exit from the cell cycle and activation of survival pathways. Step 8: tumor cells are reactivated, allowing for their outgrowth and colonization at the secondary site. Abbreviations: MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; u-PA, urokinase plasminogen activator; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.