Fig. 13.
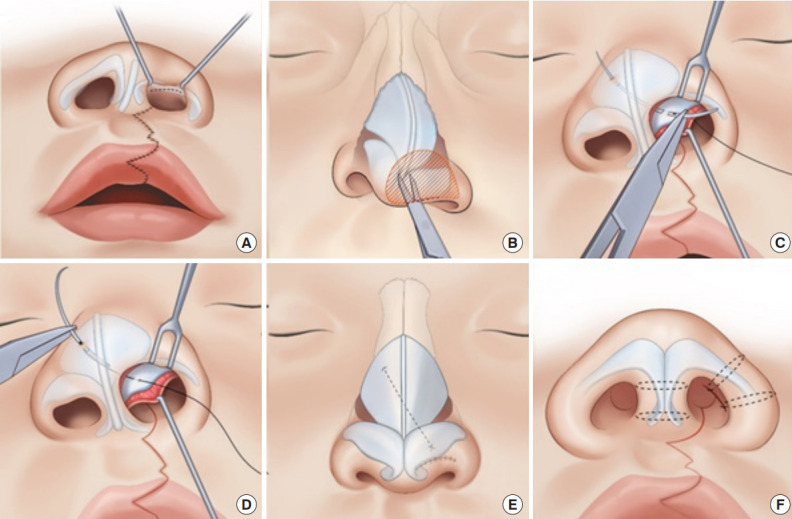
Primary cleft rhinoplasty with a custom suture needle for alar cartilage repositioning. (A, B) Through a semi-open rhinoplasty approach in the cleft side nostril, the nasal envelope is dissected from the dome of the alar cartilage and nasal tip. (C, D) The dome of alar cartilage is sutured using a Chang’s needle attached with a 5-0 polypropylene thread; the needle is then passed toward the medial and cranial sides, piercing through the septal cartilage and contralateral upper lateral cartilage. (E, F) The needle is pulled out of the skin until the laser mark is identified and then returned into the intranasal side. Transfixion sutures are made in the columella and lower lateral cartilage to minimize dead space. Reprinted from Kim et al. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2023 Jun 19 [Epub]. http://doi.org/10.1177/10556656231183383 [20].
