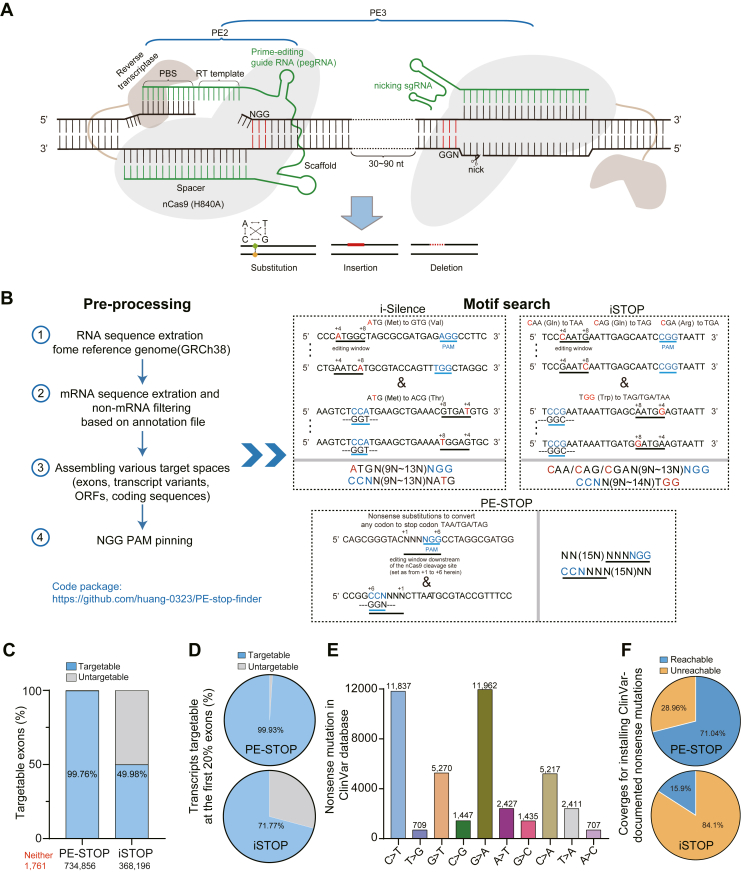
Figure 1.
The PE-STOP strategy is predicted to feature expanded genome coverages for gene inactivation and precise installation of nonsense mutations.A, a schematic view for the targeting actions by PE is shown. The nCas9 and reverse transcriptase motifs of PE are indicated. The nicked target DNA is depicted, with the PAM sequence (NGG) indicated. The pegRNA molecule is shown in green. The segments corresponding to the spacer, scaffold, RTT, and PBS are respectively marked. The left portion summarizes the PE2 components. For PE3, a nearby nicking sgRNA (canonical guide RNA) targeting the opposite strand is depicted on the right. PE enables installation of base conversions, small insertions, and small deletions. B, overall workflow for bioinformatic identification of PE-STOP, iSTOP, and i-Silence targetable sites in the human genome (under NGG PAM) is presented. The assembly of various target spaces is summarized on the left. Queries would be respectively made against all genes, transcripts, exons, and predicted ORFs. The sequence motifs used for searching editable sites by various editors are presented within the box on the right. In these boxes, examples of target sequences and generalized motifs are both presented. C, predicted percentages of human exons targetable by PE-STOP or iSTOP are presented. The targetable portions are shown in light blue, whereas the nontargetable portions are shown in gray. The numbers of exons targetable by the PE-STOP or iSTOP are marked under the columns. The number of exons untargetable by either strategy is denoted in red. D, the coverage of early exons (the number of exons included in each query = 1/5 × total number of exons in a given transcript, rounded up to the next whole number) in the human genome by PE-STOP or i-STOP strategy. The respective percentages are marked in each pie plot. E, the distribution of various types of base substitution in ClinVar database–recorded nonsense mutations is presented in a histogram. The number of records for each category of mutated alleles are marked on the columns. F, the coverages by PE-STOP or iSTOP for installing the ClinVar-documented pathogenic nonsense mutations are presented. The motif used for searching the iSTOP site is described in the text. The motif for PE-STOP was extended to including sequence from +1 to +9 after the cleavage site. The percentages of reachable and unreachable sites by PE-STOP and iSTOP are shown in the pie charts. PBS, primer-binding site; PE, prime editor; pegRNA, prime editing guide RNA; RTT, reverse transcription template; sgRNA, single-guide RNA.