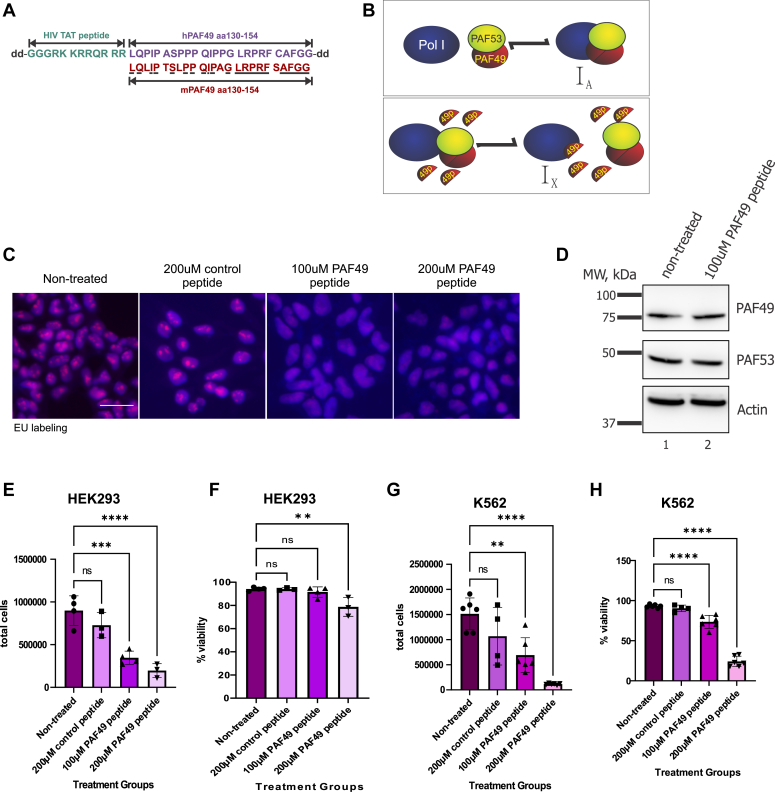
Figure 11.
Transduction of a peptide containing amino acids 130 to 154 of PAF49 can inhibit rRNA synthesis in cells.A, sequence of the hPAF49 peptide designed to inhibit rDNA transcription. The 2 d’s at the N- and C-terminal of the peptide represent d-alanine’s. The HIV TAT peptide sequence used to promote the transduction of the peptide into cells is in green. The hPAF49 sequence used to construct the peptide is in purple (aa130–154). A comparison of the mPAF49 sequence is in red. Identical amino acids between sequences are underlined in black. The peptide was provided from Peptide 2.0. B, the proposed mechanism of action of the PAF49 peptide. IA represents active polymerase and IX represents inactive polymerase. When the PAF49 peptide competitively binds to polymerase (A127), the heterodimer will no longer be able to associate with polymerase, leaving it inactive. C, HEK293 cells were treated with 100 to 200 μM of peptide or vehicle for 24 h. After 24 h, the cells were pulsed with 5-EU for 15 min and de novo synthesized RNA was visualized as described (red) against a DAPI background. Scale bar = 50 μm. D, HEK293 cells were treated ± 100 μM of peptide for 24 h and harvested as previously described. The levels of hPAF49 and hPAF53 were determined via Western blot analysis. E, HEK293 cells were treated with 100 to 200 μM of peptide or vehicle for 48 h. After 48 h, the cells were counted as described (79). Total cells/ml is displayed as mean ± SD. F, trypan blue exclusion was used to count live cells and measure percent viability within the cell population. Percent viability is displayed as mean ± SD. G, K562 cells were treated with 100 to 200 μM of peptide or vehicle for 48 h. After 48 h, the cells were counted as described (79). Significance was determined via a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The error bars represent mean ± S.D; ∗∗ <0.01 and ∗∗∗∗<0.0001. H, trypan blue exclusion was used to count live cells and measure percentage viability within the cell population. Significance was determined via a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison tests. The error bars represent mean ± SD; ∗∗∗∗<0.0001.