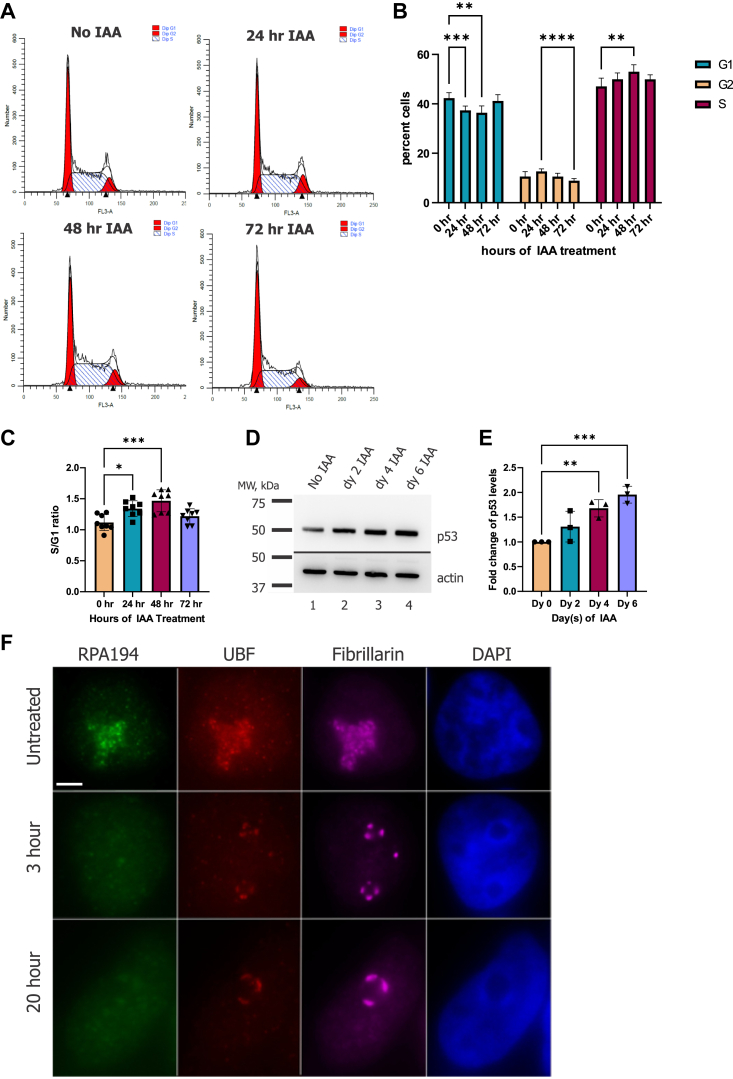
Figure 3.
Depletion of PAF49 does not cause cell cycle arrest in a specific phase.A, FACS analysis of cells at the indicated times post-treatment of IAA. B, quantification of the distribution of cells in G1, S, or G2 following IAA treatment. Four independent repeats of the analyses presented in (A) were each carried out in duplicate. The data were analyzed by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. C, ratio of cells in S and G1 was calculated for the data presented in (B). Significance was determined by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. D, Cells containing AID-PAF49 were treated with 1 mM IAA or vehicle for up to 6 days. On days 0, 2, 4, and 6, cells were harvested and lysed in HEPES lysis buffer. The expression of p53 was determined by Western blot analysis with anti-p53 antibody. E, three independent repeats of the Western blot data presented in (D) were performed. The levels of p53 were corrected for the signal of the housekeeping protein β-actin. The data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s multiple comparisons test. The error bars represent mean ± SD; ∗ = 0.05 to 0.01, ∗∗ <0.01, ∗∗∗ <0.001, ∗∗∗∗ <0.0001. F, cells containing AID-PAF53 were treated with 500 μM IAA for 3 h and 20 h. Reduction of PAF53 shows reorganization of nucleolar structures into caps along the periphery, where UBF and fibrillarin colocalize and RPA194 disperses into the nucleoplasm. Scale bar = 5 μm.