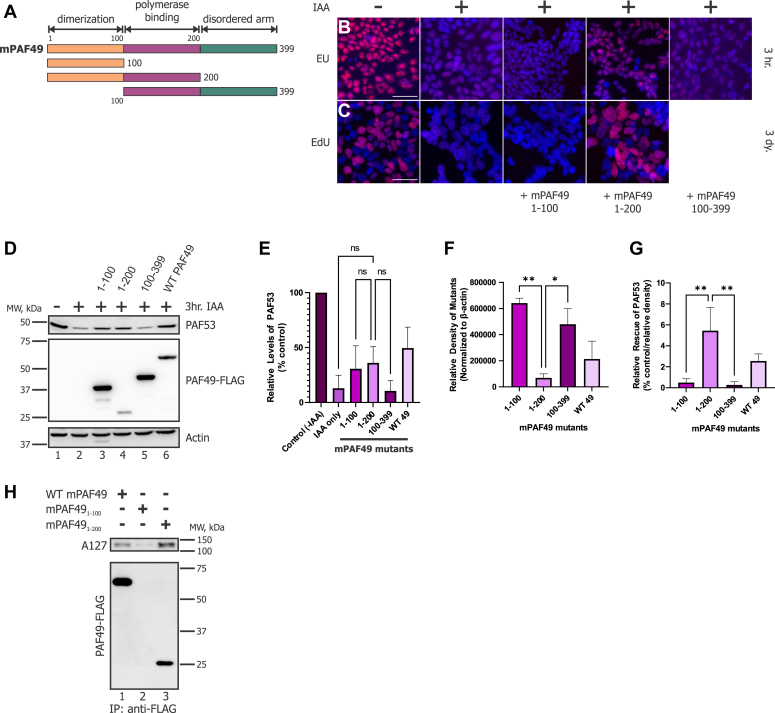
Figure 9.
The functionality of PAF49 requires the dimerization domain and adjacent sequences.A, diagrams of the mPAF49 constructs used in the following experiments. B, 24 h prior to IAA treatment, cells were transfected with the mPAF49 mutants indicated in (A). Cells were then treated with 1 mM IAA or vehicle for 3 h to knock down endogenous PAF49-AID. After 3 h, the cells were pulsed with 5-EU for 15 min and de novo synthesized RNA was visualized as described (red) against a DAPI background (94). Scale bar = 50 μm. C, to assess cell proliferation via active DNA replication, cells were treated with 1 mM IAA or vehicle for 3 days instead of 3 h as done in (B). Cells were then pulsed with EdU for 1 h and newly synthesized DNA was visualized as described (red) against a DAPI background. Scale bar = 50 μm. D, cells were transfected with either WT mPAF49 or one of the mPAF49 mutants described in A 24 h prior to IAA treatment. After 3 h of 1 mM IAA treatment, cells were harvested and lysed as described. The levels of hPAF53 and the mPAF49 mutants were determined via Western blot analysis. All mPAF49 constructs were tagged with the FLAG epitope. mPAF491-100 is also tagged with the GST epitope in order to make the protein large enough to detect on a Western blot. This explains why mPAF491-100 has a larger molecular weight than mPAF491-200. E, three independent repeats of the WB data presented in (D) were performed. The relative levels of PAF53 were quantified and corrected with β-actin. The data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; ns indicates p > 0.05. F, for the WB data presented in (D), the relative expression levels of the ectopically expressed mPAF49 mutants (and WT). They were quantitated and normalized to β-actin. Significance was determined via a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The error bars represent mean ± SD; ∗ = 0.05 to 0.01 and ∗∗ <0.01. G, to assess how well each mPAF49 mutant was able to rescue the level of PAF53 in the absence of endogenous PAF49, relative rescue of PAF53 was calculated for each construct (% control/relative density ∗ 1E4). This calculation resulted in an integer that could be used to compare the activity of each mutant. Significance was determined via a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test. The error bars represent mean ± S.D; ∗ = 0.05 to 0.01 and ∗∗ <0.01. H, HEK293 cells were transfected with the indicated FLAG-PAF49 mutant. 48 h later, the cells were lysed, and the FLAG-tagged proteins recovered with immobilized anti-FLAG antibodies and analyzed by western blotting for FLAG and A127. PAF49 1 to 100 did not blot well (lane 2).