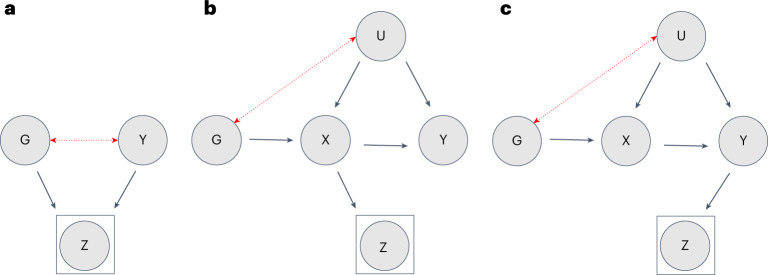
Fig. 1. The impact of participation bias in genetic studies.
a–c, The relationships between a genetic variant (G), an exposure (X) or outcome (Y), and study participation (Z). Panel a illustrates the effect of participation bias in GWA studies, where Z is a common consequence of G and Y (red dotted line). Conditioning on a common consequence (Z) induces a non-causal association between G and Y. Panels b,c illustrate the effect of participation bias in MR studies, where bias occurs if Z is a consequence of either X (b) or Y (c). Conditioning on Z induces an association between the genetic variant and confounders, thereby violating the MR assumption of exchangeability. This figure is a simplified illustration of how participation bias can impact results obtained from two commonly employed methods in genomic studies. For further examples illustrating the impact of selection bias, see Hernán et al.7.