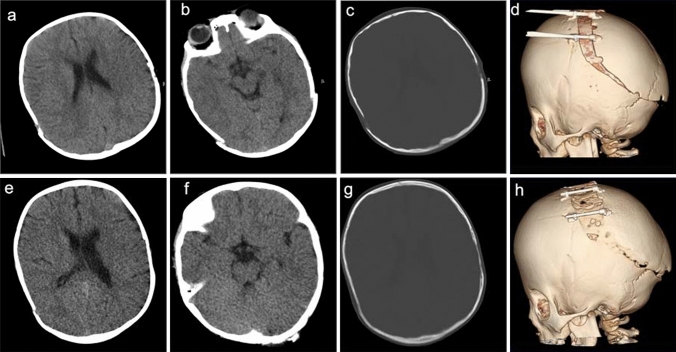
Fig. 4.
Example of comparison: four categories of view-points in the half-dose method (HDM) and full-dose method (FDM). A 4-year-old female with coronal suture craniosynostosis. Cranial computed tomography (CT) image obtained soon after cranioplasty by the FDM (a–d), and follow-up CT imaged obtained using the HDM at 4 months after the previous CT (e–h). FDM scan parameters: tube voltage, 120 kV; tube current, 220 mA; CTDI-vol, 24.4 mGy; DLP, 589.1 mGy・cm. HDM scan parameters: tube voltage, 120 kV; tube current, 130 mA; CTDI-vol, 12.5 mGy; DLP, 257.8 mGy・cm. In terms of image quality, the brain parenchyma on images obtained by the HDM (e) was relatively coarse as compared to that on images obtained by the FDM (a). However, the corticomedullary boundary of the cerebral hemisphere can be recognized on the HDM image (e). Additionally, the ventricular system (a, e), and 2D (c, g) and 3D (d, h) cranium images seemed to have a similar image quality in HDM and FDM images, without loss of diagnostic value