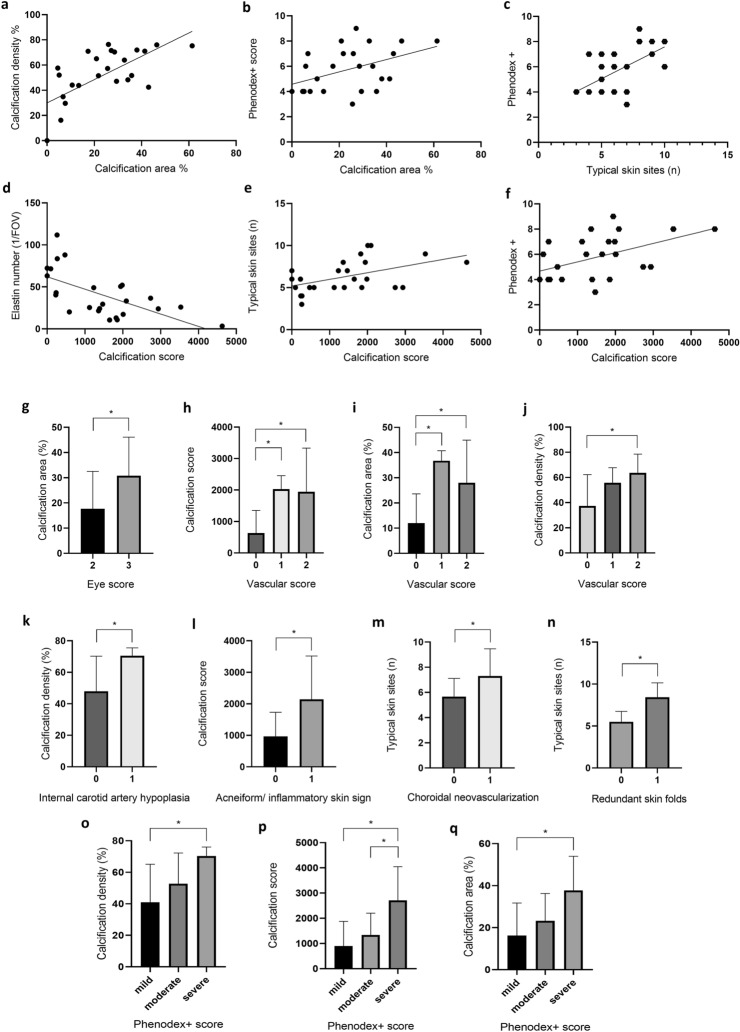
Fig. 3.
Correlation between skin calcification parameters and macroscopic skin signs or clinical phenotypes in all PXE patients. Here, statistical analyses with significant findings (p < 0.05) are represented. a positive correlation between calcification density (CD) and calcification area (CA), b positive correlation between Phenodex score and calcification area (CA), c positive correlation between Phenodex score and the number of affected typical skin sites. d inverse correlation between the number of elastic fibers (per FOV) and calcification score (CS), e positive correlation between the number of affected typical skin sites and CS, f positive correlation between Phenodex score and CS. Significantly higher CA was found in patients with more severe eye complications (E3 vs E2) (g) and significant differences were found in CS (h), CA (i) and CD (j) between patient groups with different Vascular-scores, respectively. Significantly higher CD was found in patients with internal carotid artery hypoplasia (k), significantly higher CS was found in patients with acneiform skin signs (l). m The number of affected characteristic skin sites was significantly higher in patients with choroidal neovascularization. n The number of affected characteristic skin sites was significantly higher in patients with redundant skin folds. Regarding the Phenodex + scores, significantly higher CD (o), CS (p) and CA (q) were found in patients with severe PXE compared to mild PXE, respectively. Statistical significance (p < 0.05) is marked with *