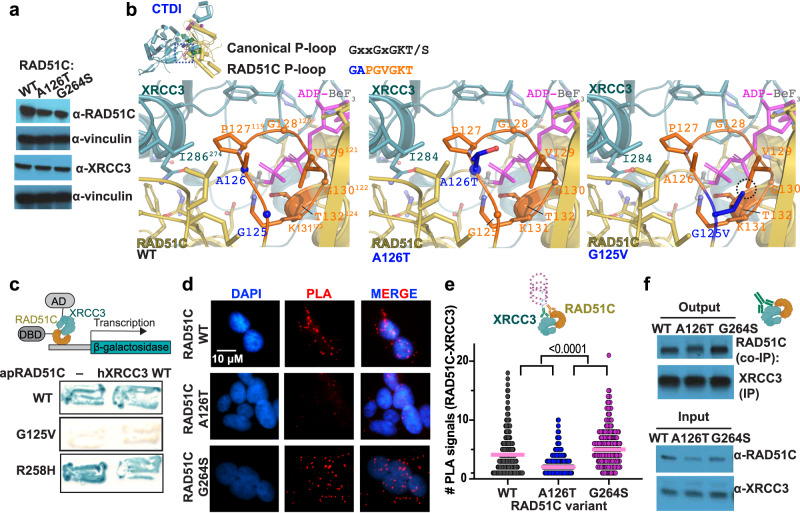
Fig. 3. CX3 CTDI mediates RAD51C-XRCC3 paralog binding.
a Western blot of HAP1 cells and variant RAD51C as indicated against RAD51C, XRCC3, or Vinculin as loading control. Representative image from 3 independent biological experiments. b Zoomed view of the structural environment of wild-type (WT) CX3 A126 and G125 (left) plus models of the RAD51C A126T (middle) and G125V (right) mutations, with mutated residues in blue and major clashes highlighted by a dashed circle. Top left, ATPase P-loop (orange with blue denoting variant positions) with the canonical and conserved RAD51C sequences. c Yeast two-hybrid assay testing interactions between wild-type (WT), G125V and R258H A. pompejana RAD51C (apRAD51C) and human XRCC3 (hXRCC3). Top, graphical sketch of two-hybrid assay adapted from http://BioRender.com. d Representative images of RAD51C-XRCC3 proximity ligation assay (PLA, red) in human HAP1 cells containing indicated variant RAD51C. DAPI denotes nucleus. e Quantification of RAD51C-XRCC3 PLA signals with hydroxyurea (200 µM) from (d), pink bar denotes median. P values (<0.0001 between all variants) were calculated using an unpaired two-sided Student T-test, n(WT) = 494, n(A126T) = 601, n(G264S) = 242, derived from 4 independent biological experiments, top, graphical schematic of a PLA reaction created with http://BioRender.com. f Immunoprecipitation (IP) of XRCC3 from HAP1 cell extracts expressing wild-type (WT), A126T or G264S RAD51C and Western blot against RAD51C Co-IP. A representative immunoblot from 3 independent experiments is shown. Schematic created with http://BioRender.com.