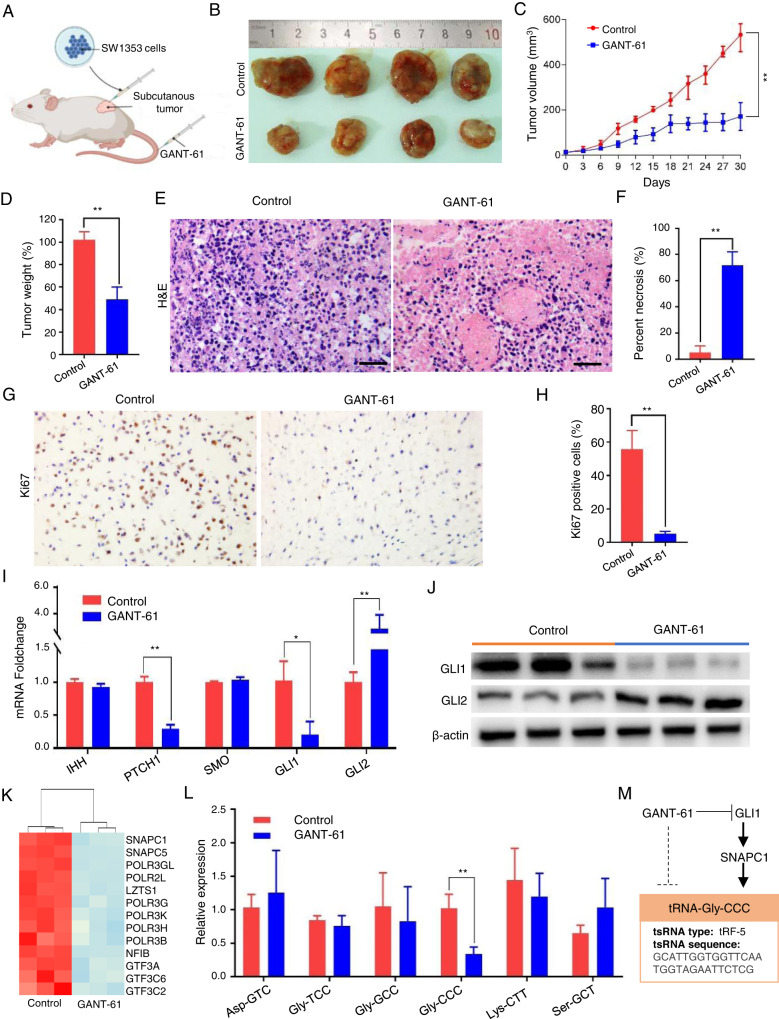
Fig. 3. GLI1 inhibitor (GANT-61) suppressed chondrosarcoma by inhibiting the RNAP III signal pathway and tRNA-Gly-CCC synthesis in vivo.
A Establishment of an in vivo xenograft mouse model. B Representative images of xenograft tumors. C Mice were treated with or without GANT-61 intravenous injection per three days for six times. Tumor volume growth curve was measured per three days for one month (**P < 0.01). D Tumor weights of mice from different treatment regimens (**P < 0.01). E Tumor tissue necrosis with or without GANT-61 detected by H&E staining. Five representative fields at a 400-fold magnification were counted per animal. F The mean necrosis rate between GANT-61 treated animals and the control group (**P < 0.01). G Tissue sections from GANT-61 treated animals and the control group were subjected to IHC analysis for Ki-67. H The number of Ki-67 positive cells was compared between GANT-61 treated animals and the control group (**P < 0.01). I mRNA expression changes of IHH, PTCH1, SMO, Gli1, and Gli2 were detected using qPCR in the two groups (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). J Western blot (WB) analysis was performed to assess the protein expression levels of Gli1, and Gli2. K Heat map of hub genes of RNAP III transcription signal pathway. L Relative expression of tRNA-Asp-GTC, tRNA-Gly-TCC, tRNA-Gly-GCC, tRNA-Gly-CCC, tRNA-Lys-CTT, tRNA-Ser-GCT (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). M Illustration of the relationship among Hedgehog-GLI1 signal, RNAP III transcription signal pathway, and tRNA-Gly-TCC.