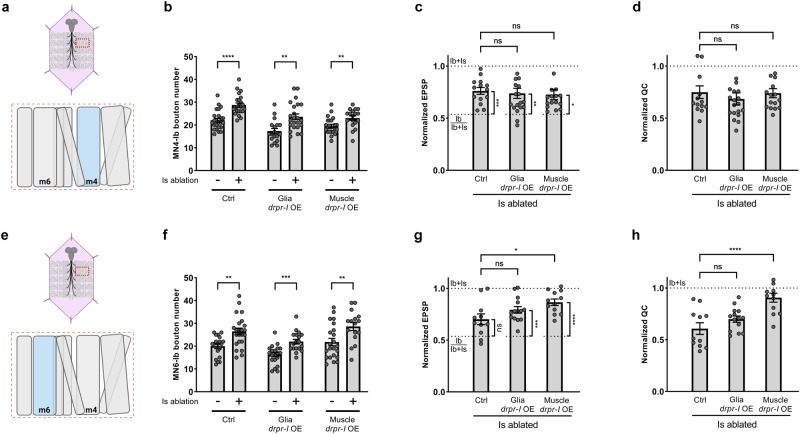
Fig. 5. Overexpression of Draper-I boosts cross-neuron plasticity of MN6-Ib.
a Cartoon representation of a dissected larva (pink) and a hemisegment highlighted by dashed red rectangle. The target muscle examined in (b–d) is shown in blue. Cartoon is generated with Biorender. b Quantification of MN4-Ib bouton number in non-ablated and Is ablated larvae in control, glia draper-I overexpression, and muscle draper-I overexpression backgrounds. Control (N = 24 and 23 NMJs), t(45) = 5.321, p < 0.0001, unpaired t test, two-tailed. Glia draper-I overexpression (N = 18 and 23 NMJs), t(39) = 3.557, p = 0.001, unpaired t test, two-tailed. Muscle draper-I overexpression (N = 23 and 18 NMJs), t(39) = 2.844, p = 0.0071, unpaired t test, two-tailed. c Quantification of normalized EPSP of MN4-Ib in Is ablated larvae in control, glia draper-I overexpression, and muscle draper-I overexpression backgrounds. F(2, 46) = 0.8117, p = 0.4504, One-way ANOVA. Is ablated control vs glia draper-I overexpression, p = 0.9333. Is ablated control vs muscle draper-I overexpression, p = 0.8633. Is ablated control vs Ib/Ib+Is, t(24) = 4.335, p = 0.0002, unpaired t test, two-tailed. Is ablated in glia draper-I overexpression vs Ib/Ib+Is, t(28.3) = 3.001, p = 0.0056, unpaired t test, two-tailed, with Welch’s correction. Is ablated in muscle draper-I overexpression vs Ib/Ib+Is, t(26) = 2.547, p = 0.0171, unpaired t test, two-tailed. d Quantification of normalized quantal content of MN4-Ib in Is ablated larvae in control, glia draper-I overexpression, and muscle draper-I overexpression backgrounds. F(2, 46) = 0.1383, p = 0.8712, One-way ANOVA. Is ablated control vs glia draper-I overexpression, p = 0.6839. Is ablated control vs muscle draper-I overexpression, p = 0.9923. For (c, d) N (NMJs) = 14, 19, 16. e Cartoon representation of a dissected larva (pink) and a hemisegment highlighted by dashed red rectangle. The target muscle examined in (f–h) is shown in blue.. Cartoon is generated with Biorender. f Quantification of MN6-Ib bouton number in non-ablated and Is ablated larvae in control, glia draper-I overexpression, and muscle draper-I overexpression backgrounds. Control (N = 19 and 23 NMJs), t(40) = 3.493, p = 0.0012, unpaired t test, two-tailed. Glia draper-I overexpression (N = 20 and 18 NMJs), t(36) = 4.103, p = 0.0002, unpaired t test, two-tailed. Muscle draper-I overexpression (N = 22 and 16 NMJs), t(36) = 2.818, p = 0.0078, unpaired t test, two-tailed. g Quantification of normalized EPSP of MN6-Ib in Is ablated larvae in control, glia draper-I overexpression, and muscle draper-I overexpression backgrounds. F(2, 34) = 4.361, p = 0.0206, One-way ANOVA. Is ablated control vs glia draper-I overexpression, p = 0.2235. Is ablated control vs muscle draper-I overexpression, p = 0.0153. Is ablated control vs Ib/Ib+Is, t(19) = 2.074, p = 0.0519, unpaired t test, two-tailed. Is ablated in glia draper-I overexpression vs Ib/Ib+Is, t(22) = 4.041, p = 0.0005, unpaired t test, two-tailed. Is ablated in muscle draper-I overexpression vs Ib/Ib+Is, t(20) = 5.061, p < 0.0001, unpaired t test, two-tailed. h Quantification of normalized quantal content of MN6-Ib in Is ablated larvae in control, glia draper-I overexpression, and muscle draper-I overexpression backgrounds. F(2, 34) = 12.27, p < 0.0001, One-way ANOVA. Is ablated control vs glia draper-I overexpression, p = 0.2951. Is ablated control vs muscle draper-I overexpression, p < 0.0001. For (g, h), N (NMJs) = 11, 14, 12. Error bars indicate ± SEM, ns = non-significant, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.