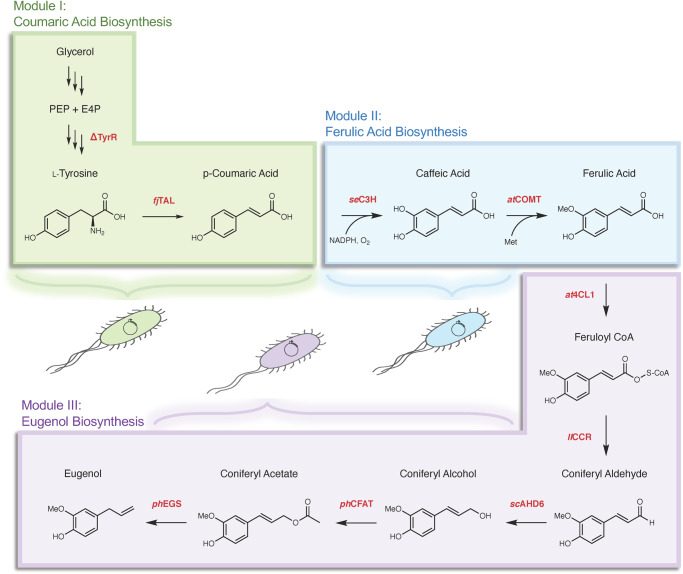
Fig. 1. Overview of biosynthetic pathway and tripartite modular scheme for phenylpropene synthesis.
Module I (coumaric acid biosynthesis module) includes modifications to boost intracellular tyrosine flux, as well as heterologous expression for efficient conversion of L-tyrosine to p-coumaric acid. Module II (ferulic acid biosynthesis module) incorporates heterologous enzymes with high efficiency for conversion of hydroxycinnamic acid substrates to ferulic acid in bacteria. Module III (eugenol biosynthesis module) includes heterologous enzymes for conversion of hydroxycinnamic acid substrates to phenylpropenes with high efficiency. Heterologous enzymes: fjTAL, tyrosine ammonia lyase from F. johnsoniae; seC3H, p-coumarate-3-hydroxylase from S. espanaensis; atCOMT, caffeic acid-o-methyltransferase from A. thaliana; at4CL1, 4-coumarate-CoA ligase from A. thaliana; llCCR, cinnamoyl-CoA reductase from L. leucocephala; scADH6, alcohol dehydrogenase 6 from S. cerevisiae; phCFAT, coniferyl alcohol acyltransferase from P. hybrida; phEGS, eugenol synthase from P. hybrida.