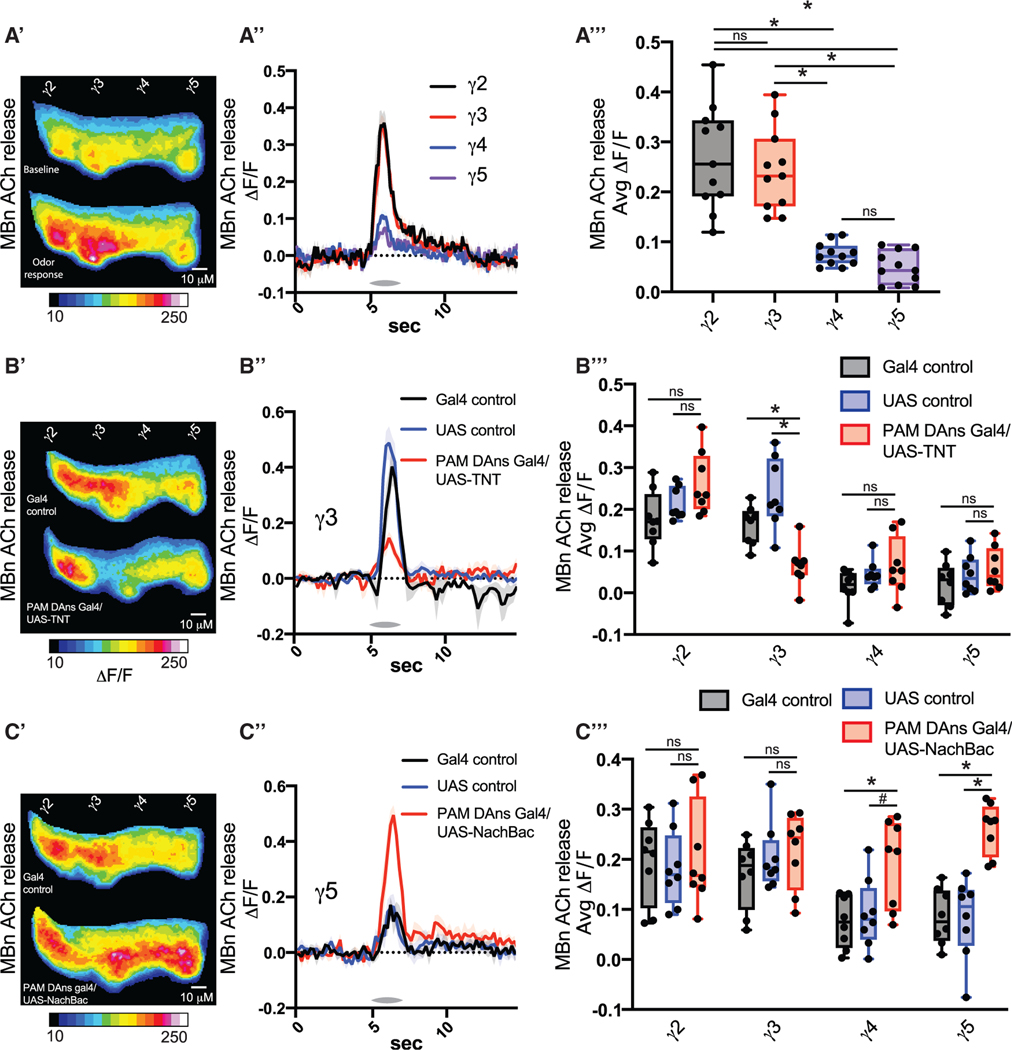
Figure 2. Dopamine controls MBn neurotransmission.
(A) The GRAB ACh sensor was expressed in MBns using R13F02-gal4. One second of odor (MCH) was delivered at 5 s. n = 11.
(A′) Mean time series projection of GRAB ACh fluorescence for baseline, across 2 s prior odor delivery; for odor response, across 2 s starting at odor delivery. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(A″) Traces show the average response (±SEM, shading) across all flies tested.
(A″′) Average odor responses were quantified for each compartment.
(B) The GRAB ACh sensor was expressed in MBns using R13F02-LexA, and TNT was expressed in PAM DANs using R58E02 gal4. One second of odor (MCH) was delivered at 5 s. n = 8.
(B′) Mean time series projection of GRAB ACh fluorescence for odor responses, across 2 s starting at odor delivery. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(B″) Traces show the average odor (MCH) response (±SEM) across all flies tested in γ3.
(B″′) Average odor (MCH) responses were quantified for each compartment.
(C) The GRAB ACh sensor was expressed in MBns using R13F02-LexA, and NachBac was expressed in PAM DANs using R58E02 gal4. n = 8.
(C′) Mean time series projection of GRAB ACh fluorescence for odor (MCH) responses, across 2 s starting at odor delivery. Scale bar, 10 μm.
(C″) Traces show the average response (±SEM) across all flies tested in γ5.
(C″′) Average odor responses were quantified for each compartment in γ2–5.
Box-and-whisker plots showthe range of individual data points, with the interquartile spread as the box and the median as the line bisecting each box. *p < 0.05.
(A) One-way ANOVA with Dunn′s test. (B and C) One-way ANOVA with Kruskal-Wallis test.