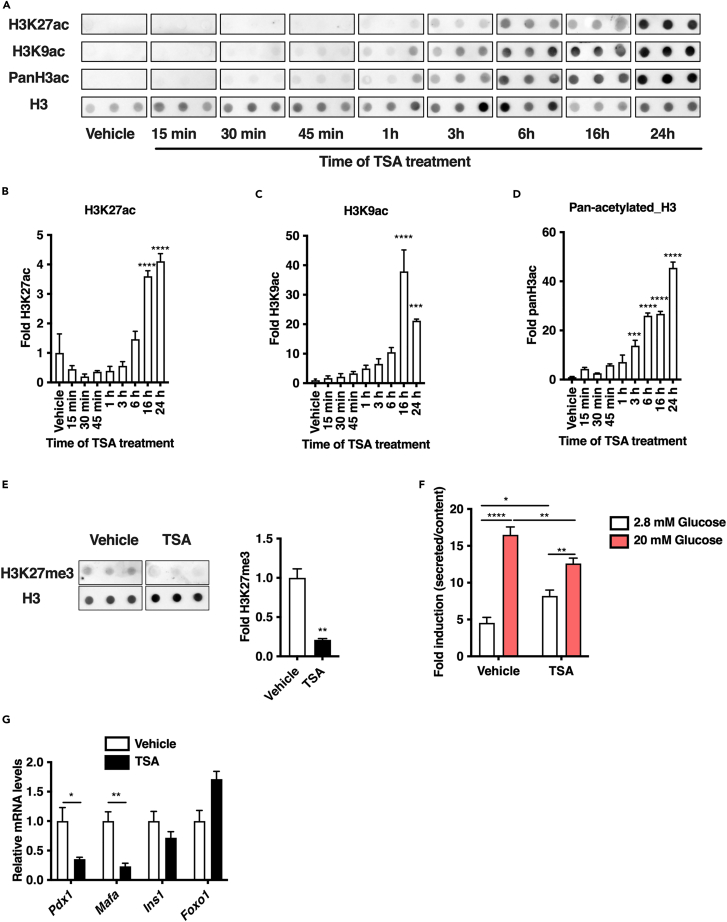
Figure 1.
The increase of histone H3 acetylation level on TSA treatment is correlated with alteration of functional properties of Min6 cells
(A) Dot blot kinetic analysis of H3K9ac, H3K27ac and pan-acetylated histone H3 (Pan H3ac) levels on TSA treatment (0.5 μM) in Min6 cells at the indicated time (n = 3). Vehicle (DMSO 0.1%) was used as negative control.
(B–D) Signals were normalized to total H3 signals and densitometry analysis of A was performed by comparing the mean of signal at each time point to mean signal in vehicle (n = 3).
(E) Dot blot analysis of H3K27me3 levels on TSA treatment (0.5 μM, 16 h) in Min6 cells. Vehicle (DMSO 0.1%) was used as negative control. Signals were normalized to total H3 signals and densitometry analysis is expressed as fold of H3K27me3 signals in TSA-treated cells compared to signals in vehicle-treated cells (n = 3).
(F) Glucose-stimulated insulin secretion of TSA-treated cells (0.5 μM, 16 h, n = 7). Vehicle (DMSO 0.1%) was used as a control. Results are presented as fold insulin secretion in response to 20 mM glucose compared to 2.8 mM glucose +/−SEM.
(G) Quantitative RT-PCR analysis of key β-cell identity genes in vehicle and TSA-treated Min6 cells (n = 3).
Results in B, C, D, E, F, G, are displayed as means +/−SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.
See also Figure S1.