Figure 3.
Pre-encapsulation variables affect scRNA-seq data quality and cell type diversity
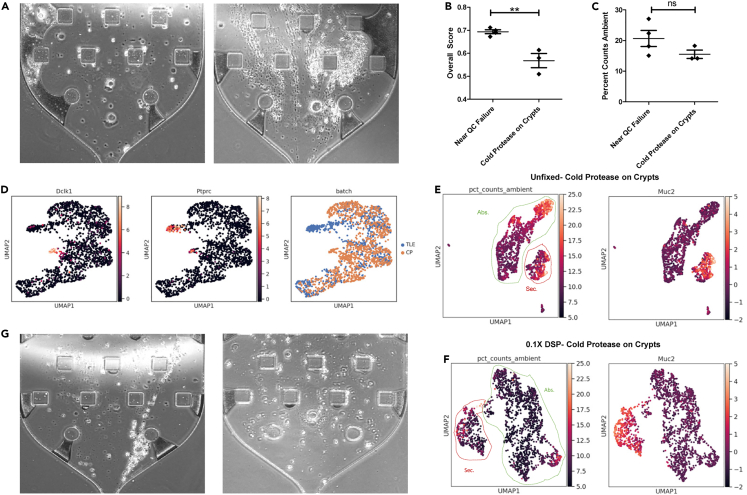
(A) Live hopper visualization of (left) viable single cells and (right) dying cells.
(B and C) Quantification of (B) AmbiQuant overall score, (C) percent counts ambient comparing near QC failure runs (MACs enzyme on minced tissue, cold protease on minced tissue, MACs enzyme on minced, and Collagenase/DNase on Crypts) and cold protease dissociation on crypts. Mean with SEM as error bars for n = 3 or 4 samples. ∗∗p < 0.01 by t-test.
(D) UMAP embedding of filtered cells from (blue) TrypLE and (orange) cold protease datasets. Expression of Dclk1, a tuft cell marker, and Ptprc, an immune cell marker, were overlaid.
(E and F) UMAP overlay with percent counts ambient or Muc2 expression for (E) unfixed cells or (F) fixed cells prepared with cold protease dissociation on crypts. Secretory (red) and absorptive (green) lineages are outlined. Gene expression values on scale bars are Z-scores of normalized values described in STAR Methods.
(G) Live hopper visualization of (left) unfixed cells and (right) cells fixed with 0.1 X DSP.