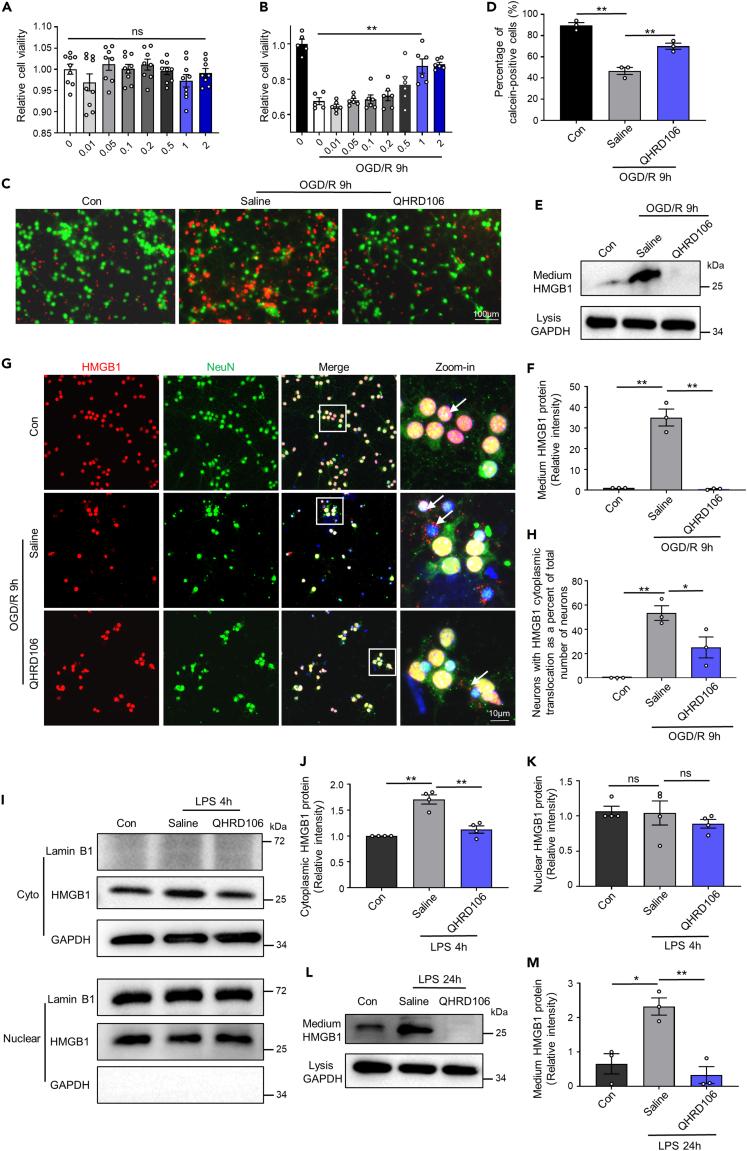
Figure 5.
QHRD106 decreases neuronal and microglial HMGB1 secretion in vitro
(A and B) The CCK-8 method was used to determine the cell viability of in vitro primary neurons with the addition of 0–2 μM QHRD106. In addition, 1 μM QHRD106 was selected for in vitro experiments.
(C and D) The apoptosis of primary cortical neurons after OGD/R was evaluated by calcein-AM and PI dual labeling. Scale bar: 100 μm. Green fluorescent calcein-AM-positive cells indicated cell survival, and the percentage of these cells was calculated. n = 3/group. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.
(E) Representative western blot images of medium HMGB1 and cell lysate GAPDH in primary cortical neurons 9 h after OGD/R.
(F) Quantification of medium HMGB1 expression.
(G and H) Immunofluorescence of HMGB1 (red) in neuronal cells (NeuN+; green) in primary cortical neurons 9 h after OGD/R. The arrows point to the location of HMGB1. The low-magnification illustration in the white box is displayed in the high-magnification view in the right column. DAPI staining is shown in blue, n = 3/group. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post hoc test.
(I–K) The nucleocytoplasmic translocation of HMGB1 in primary microglia 4 h after LPS (100 ng/mL) stimulation was evaluated by western blot analysis. GAPDH and Lamin B1 were used as cytoplasmic and nuclear loading controls, respectively.
(L) Representative western blot images of medium HMGB1 and cell lysis GAPDH in primary microglia 24 h after LPS stimulation.
(M) Quantification of medium HMGB1 expression.
All data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical analyses were performed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01 vs. the saline group; “ns” indicates no significance (p > 0.05).