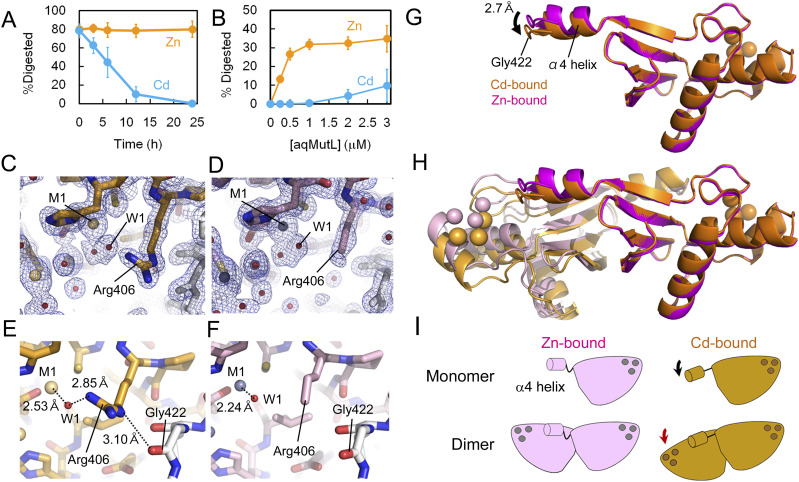
Figure 3. Cadmium ion is an inhibitor of the A. aeolicus MutL (aqMutL) endonuclease activity.
(A) aqMutL was incubated in the 0.5 mM CdCl2- or ZnCl2-containing buffer at 60°C for 0, 3, 6, 12, or 24 h. The endonuclease activity of the CdCl2- or ZnCl2-treated aqMutL (2 μM) was measured in the divalent metal-free buffer using a supercoiled plasmid DNA as the substrate at 70°C for 30 min. Average values from three independent experiments are shown with standard deviations. (B) After treatment with 0.5 mM ZnCl2 or CdCl2 at 60°C for 12 h, the endonuclease activity of aqMutL was measured at different protein concentrations in the divalent metal-free buffer at 70°C for 15 min. Average values from three independent experiments are shown with standard deviations. (C) The electron density of the side chain of Arg406 is obvious in the cadmium-bound form of the aqMutL C-terminal endonuclease domain (CTD). Blue mesh represents the 2Fo–Fc map shown at 3.0 σ. Gold and red spheres represent cadmium ions and water molecules, respectively. (D) The electron density of the guanidino group of Arg406 is missing in the zinc-bound form of the aqMutL CTD. Blue mesh represents the 2Fo–Fc map shown at 3.0 σ. (E) The guanidino group of Arg406 is fixed by a cadmium ion via the W1 water molecule in the cadmium-bound form. And Nε of Arg406 makes a hydrogen bond with the main-chain carbonyl group of Gly422. (F) No interactions involving the side chain of Arg406 were observed in the zinc-bound form. (G) Superimposition of the monomeric structures of the cadmium-bound (orange) and zinc-bound (magenta) forms of the aqMutL CTD. The cadmium-bound and zinc-bound forms were superimposed so that the positions of the three metals and the metal-coordinating residues of the subunit on the right side coincide between the two forms. Metal ions are shown in sphere models. Gly422 is located at the tip of the loop structure extending from the α4 helix of the other subunit. The α4 helix in the cadmium-bound form moved by 2.70 Å compared with that in the zinc-bound form. (H) Superimposition of the dimeric structures of the cadmium-bound (gold/orange) and zinc-bound (light pink/magenta) forms of the aqMutL CTD. (C, E, F) It should be noted that, of the two catalytic sites shown here, the one on the right side (indicated by a red arrow head) is shown in panels (C, E, F). (I) A schematic representation of cadmium-dependent structural changes in the aqMutL CTD, which depicts the movement of the α4 helix (black arrow) and the change in the subunit arrangement (red arrow).
Source data are available for this figure.