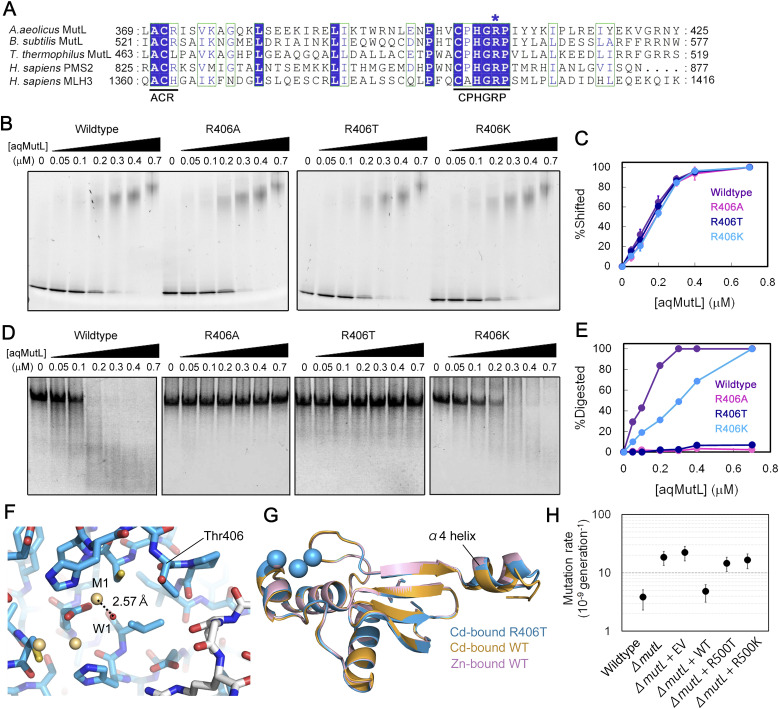
Figure 5. Arg406 is a catalytic residue for the endonuclease activity of A. aeolicus MutL (aqMutL).
(A) Amino acid sequence alignment of the C-terminal region of MutL endonucleases. The ACR and CPHGRP motifs are underlined. The conserved arginine residue corresponding to Arg406 of aqMutL is indicated by an asterisk. (B) DNA-binding abilities of the WT and mutant forms of the full-length aqMutL were examined by electrophoretic mobility shift assay. (B, C) Percentages of the shifted DNA signals in panel (B) were plotted against protein concentrations. Average values from three independent experiments are shown with standard deviations. (D) The endonuclease activity of the WT and mutant forms of aqMutL. A 60-bp double-stranded DNA was incubated with the proteins at 55°C for 60 min, and the incised products were separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions. (D, E) The ratios of digested DNA signals to all DNA signals in panel (D) were plotted against protein concentrations. (F) The catalytic site of the cadmium-bound form of the R406T aqMutL C-terminal endonuclease domain (CTD). (G) Superimposition of the overall structure of the cadmium-bound form of the R406T aqMutL CTD with those of the cadmium-bound and zinc-bound forms of the WT aqMutL CTD. (H) Phenotype complementation experiments using T. thermophilus. Mutation rates of T. thermophilus strains were estimated by the fluctuation assay based on the frequency of streptomycin-resistant cells. Experiments were performed with 17 independent cultures for each strain. Bars indicate 95% confidence intervals. EV, empty vector.
Source data are available for this figure.