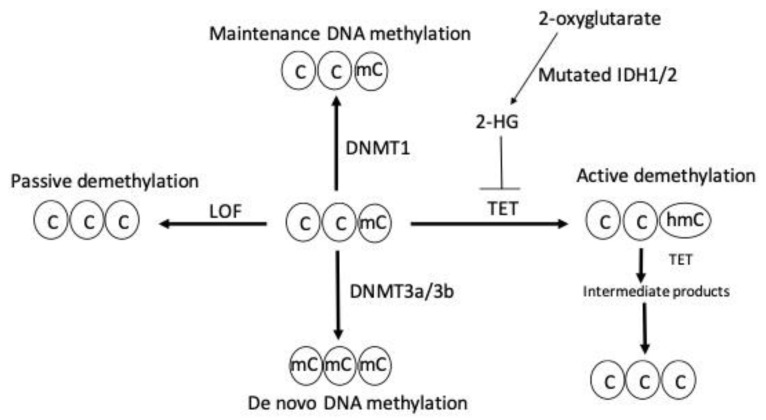
Figure 1.
DNA methylation and demethylation. Maintenance and de novo DNA methylation are catalyzed by DNMT1 and DNMT3a/3b, respectively. Loss of function (LOF) mutation of DNMT enzymes induces passive demethylation. TET enzymes catalyze active demethylation by sequential oxidation reactions that leads to the formation of sequential intermediate products, such as 5 hydroxylmethylcytosine (5 hmc), 5-formylcytosine, and, finally, 5-carboxylcytosine, which is replaced by unmodified cytosine through base excision repair. TET enzymes are inhibited by the oncometabolite 2-hydroxyglutarate (2-HG) generated by neomorphic mutations in isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH1) and IDH2 enzymes resulting in active demethylation inhibition. C indicates cytosine, mC indicates methylcytosine, and hmC indicates 5-hydroxylmethylcytosine.