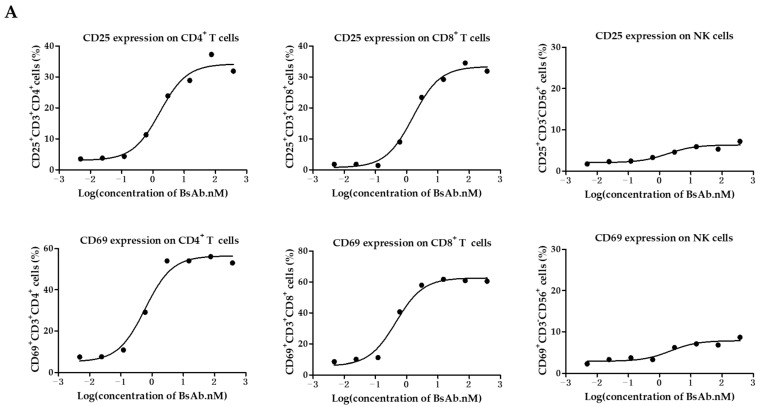
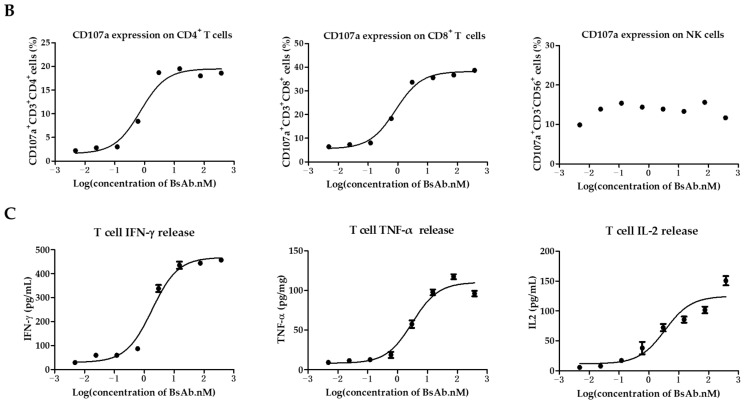
Figure 3.
MUC1/CD3 BsAb can induce robust T cell activation. (A) Detection of BsAb-induced T cell and NK cell activation (CD69 and CD25). HeLa cells were co-cultured with human PBMCs with an effector-to-target ratio of 10:1 for 24 h with serially diluted antibodies. After incubation, PBMCs were collected, stained, and analyzed for CD69 and CD25 expression via flow cytometry. (B) Detection of BsAb-induced CD107a expression on CD3+CD4+ T cells, CD3+CD8+ T cells, and NK cells. HeLa cells were co-cultured with human T cells or PBMCs with an effector-to-target ratio of 10:1 with various concentrations of BsAb as indicated, then a CD107a antibody was added to the culture medium. After another 4 h, cells were collected and analyzed for CD107a expression via flow cytometry. For detailed gating strategy of CD25, CD69, and CD107a expression, please refer to the supplementary materials. (C) Measurement of cytokine produced in the co-culture supernatant via ELISA. HeLa cells were co-cultured with human T cells with an effector-to-target ratio of 8:1 in the presence of serially diluted BsAb. After 48 h of incubation, cell-free supernatant was obtained and the secretion of IFN-γ, TNF-α, and IL-2 was detected via ELISA. The data shown here are representative of three individual experiments.